Compared with traditional materials with circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) activity, such as organic molecules, polymers, metal-organic complexes, and liquid crystals, covalent organic frameworks (COFs), as a new kind of crystalline porous materials, have a wide application potential because of their structural designability, versatility, functional adjustability, and chemical stability.
At present, COFs with CPL activity and good crystallinity have not been reported. 2D COFs with ultra-thin nanosheet structures can effectively prevent fluorescence quenching caused by π - π stacking. Introducing chiral and luminescent functions into 2D COFs is an effective way to obtain CPL materials, but it still remains a challenge.
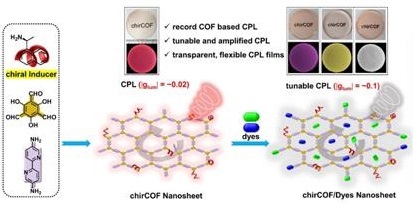
Schematic illustration of the research.
In a study published in J. Am. Chem. Soc., Prof. ZHANG Jian, Prof. GU Zhigang and their colleagues from the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have reported chiral-Induced ultra-thin chiral COFs nanosheets and their application in the field of circularly polarized luminescence.
The researchers first prepared ultrathin CO Fs nanosheets (NS) based CPL materials using a chiral induced-synthesis strategy. Chiral amines served as chiral inducers to give COF TpBpy with chirality and participated in the modification of TpBpy, inhibiting the fluorescence quenching caused by π–π stacking to form ultrathin luminescent chiral COFs (chirCOFs) NS. The obtained chirCOFs R-/S-TpBpy NS had strong chirality and intense red CPL property with a |glum| of about 0.02.
They then postmodified the carboxyl containing green and blue fluorescent dye molecules onto the chirCOFs NS (chirCOFs/Dyes) to achieve color-adjustable CPL.
Due to the chirality and energy transfer between chirCOFs and dye groups, the obtained chirCOFs/Dyes showed strong chirality and increased and tunable photoluminescence, exhibiting excellent, tunable, and amplified CPL performance with a maximum |glum| of about 0.1, which was about five times stronger than that of as-prepared chirCOFs NS.
Moreover, the researchers dispersed the corresponding chirCOFs NS into a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) matrix to form wafer size, highly transparent, and flexible COFs/PDMS films for practical CPL application.
This study opens a new strategy to prepare ultrathin chirCOFs NS with strong and tunable CPL by chiral induction and provides a new approach for the preparation of transparent, large size, and flexible COFs composite films in chiral optical applications.
Read the original article on Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
