"To put it simply, we make gold from nanocellulose," says Daniel Aili, associate professor in the Division of Biophysics and Bioengineering at the Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology at Linköping University.
The research group, led by Daniel Aili, has used a biosynthetic nanocellulose produced by bacteria and originally developed for wound care. The scientists have subsequently decorated the cellulose with metal nanoparticles, principally silver and gold. The particles, no larger than a few billionths of a metre, are first tailored to give them the properties desired, and then combined with the nanocellulose.
Three-dimensional scaffold
"Nanocellulose consists of thin threads of cellulose, with a diameter approximately one thousandth of the diameter of a human hair. The threads act as a three-dimensional scaffold for the metal particles. When the particles attach themselves to the cellulose, a material that consists of a network of particles and cellulose forms," Daniel Aili explains.
The researchers can determine with high precision how many particles will attach, and their identities. They can also mix particles of different metals and with different shapes -- spherical, elliptical and triangular.
In the first part of a scientific article published in Advanced Functional Materials, the group describes the process and explains why it works as it does. The second part focusses on several areas of application.
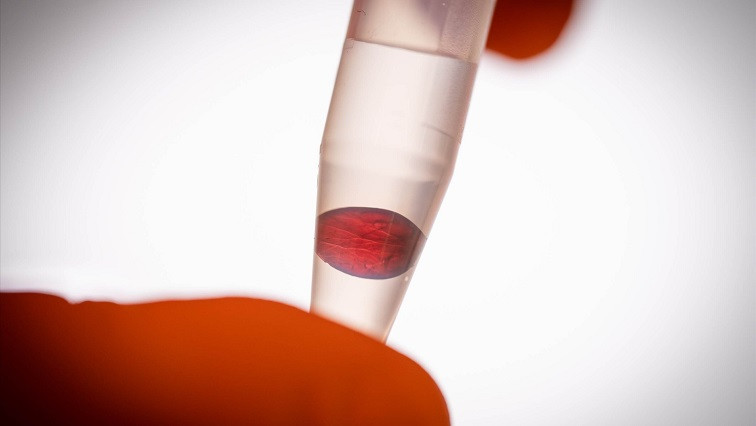
One exciting phenomenon is the way in which the properties of the material change when pressure is applied. Optical phenomena arise when the particles approach each other and interact, and the material changes colour. As the pressure increases, the material eventually appears to be gold.
"We saw that the material changed colour when we picked it up in tweezers, and at first we couldn't understand why," says Daniel Aili.
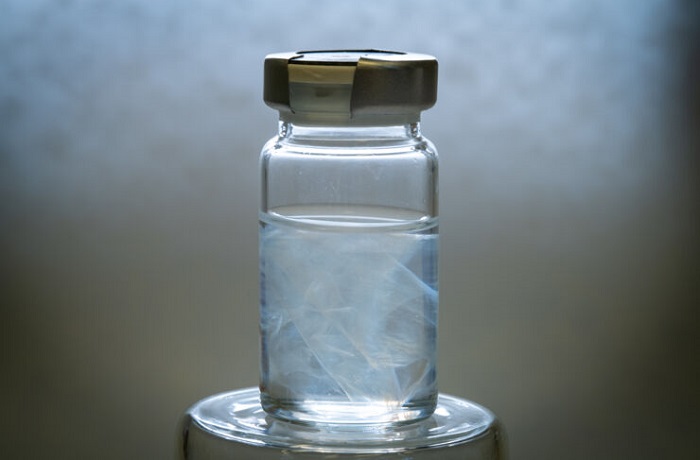

Mechanoplasmonic effect
The scientists have named the phenomenon "the mechanoplasmonic effect," and it has turned out to be very useful. A closely related application is in sensors, since it is possible to read the sensor with the naked eye. An example: If a protein sticks to the material, it no longer changes colour when placed under pressure. If the protein is a marker for a particular disease, the failure to change colour can be used in diagnosis. If the material changes colour, the marker protein is not present.
Another interesting phenomenon is displayed by a variant of the material that absorbs light from a much broader spectrum visible light and generates heat. This property can be used for both energy-based applications and in medicine.
"Our method makes it possible to manufacture composites of nanocellulose and metal nanoparticles that are soft and biocompatible materials for optical, catalytic, electrical and biomedical applications. Since the material is self-assembling, we can produce complex materials with completely new well-defined properties," Daniel Aili concludes.
Read the original article on Linköping University.