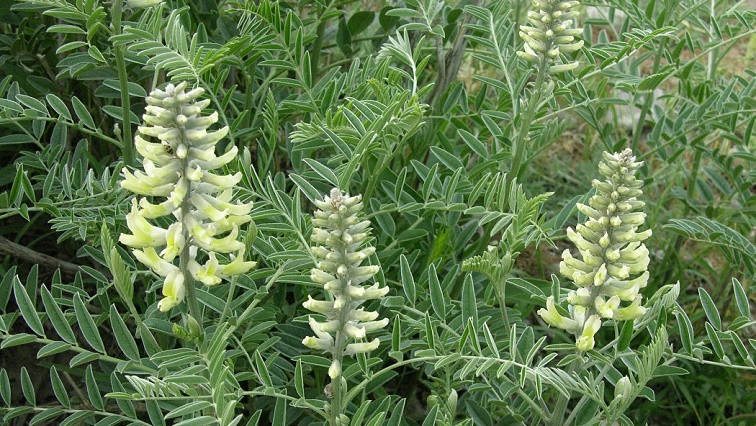
In a study published in Environmental Science: Nano, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) and their collaborators showed the promoting effects of single-walled carbon nanohorns (SWCNHs) and ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) on plant growth and salt tolerance in Sophora alopecuroides seedlings.
Physiological approaches integrated with metabolomics analysis were performed to investigate the underlying mechanisms of ZnO NP- and SWCNH mediated salt stress responses in S. alopecuroides.
The researchers showed that changes in metabolomic profiling by SWCNHs and ZnO NPs contributed to salt tolerance in Sophora alopecuroides seedlings.
Compared with untreated control plants, foliar spraying with SWCNHs increased root length, root fresh weight and leaf soluble sugar content; while ZnONPs increased root fresh weight, leaf dry weight and soluble sugar content, indicating that the two engineering nanomaterials (ENMs) improved the growth of S. alopecuroides seedlings.
"These results suggested that the application of the two ENMs provided a novel way to improve salt tolerance in plants," said Dr. WAN Jinpeng, first author of the study.
"Future study on the investigation of the changes of gene expression and metabolic profiling in full life cycle will provide stronger evidences for the use of the two ENMs in sustainable agricultural strategies for crop cultivation," added WAN.
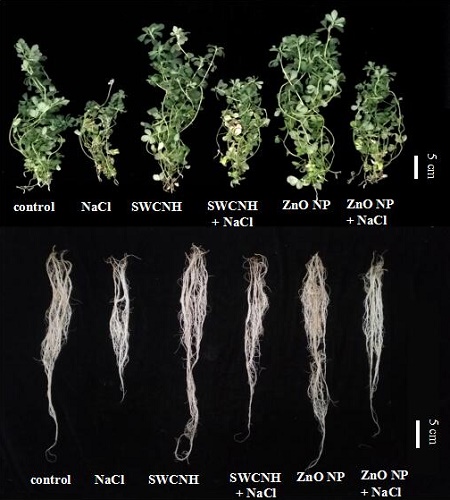

SWCNHs and ZnO NPs alleviated salt-induced growth inhibition. It shows the growth of leaves and roots.
Read the original article on Chinese Academy of Sciences.