There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
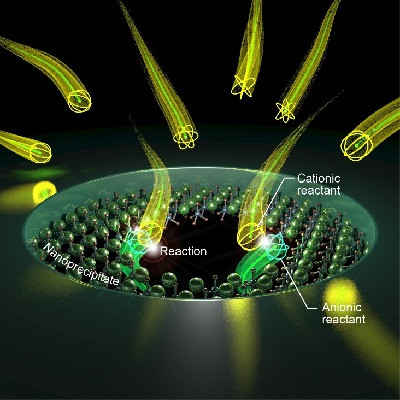
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
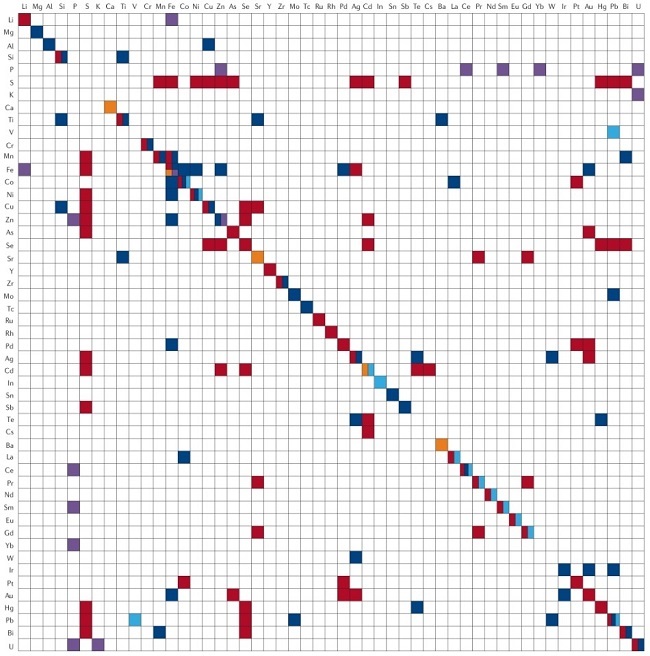
Single- and two-element map of inorganic nanomaterials biosynthesized using microbial cells and bacteriophages. Fifty-one elements (excluding H, C, N and O) have been used in inorganic nanomaterial synthesis using microbial cells and bacteriophages. White spaces indicate that biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials comprising the corresponding elements has not yet been reported. Red denotes unary or binary metal/non-metal nanomaterials that have been biosynthesized. Dark blue denotes metal/non-metal oxides that have been biosynthesized. Light blue indicates biosynthesized metal hydroxides. Light purple indicates that metal/non-metal phosphates have been biosynthesized. Orange indicates that metal carbonates have been biosynthesized. All inorganic nanomaterials biosynthesized using microbial cells and bacteriophages are listed in the paper.
Read the original article on Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST).