Although twisted sheets of double bilayer graphene have been studied extensively the past few years, there are still pieces missing in the puzzle that is its phase diagram—the different undisturbed, ground states of the system. Writing in Nature Physics, Carmen Rubio-Verdú and colleagues have found a new puzzle piece: an electronic nematic phase.
First described in another state of matter called a liquid crystal, a nematic phase occurs when particles in a material break an otherwise symmetrical structure and come to loosely orient with one another along the same axis. This phenomenon is the basis of the LCD display commonly used in televisions and computer monitors. In an electronic nematic phase, the particles in question are electrons, whose behavior and arrangement in a material can influence how well that material will conduct an electrical current in different directions.
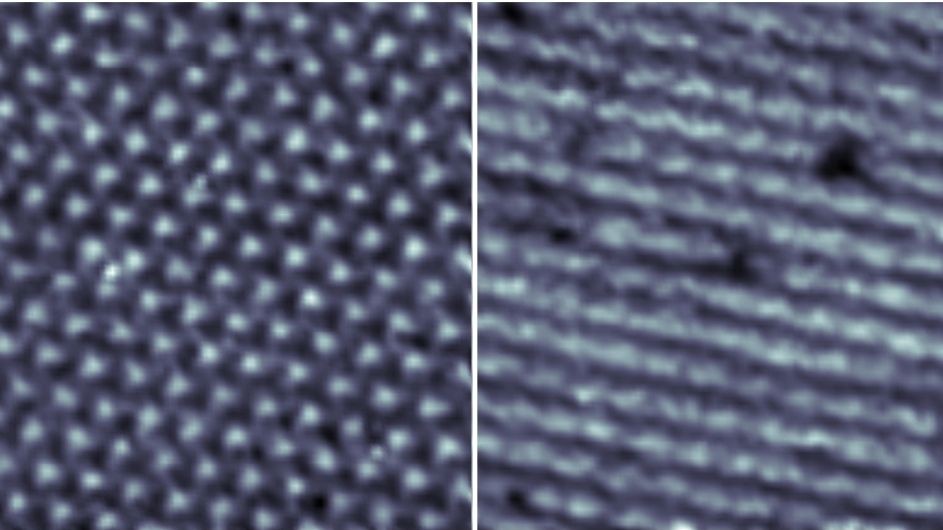
Two 200 nm-wide spectroscopy images of a sample of twisted double bilayer graphene. The left depicts the triangle lattice of the moiré material, which has three-fold symmetry and can be rotated 120 degrees any direction without changing the image. The second image was taken at a different energy level and can now only be rotated 180 degrees. The emergence of stripes reflects this broken rotational symmetry and indicates a nematic phase.
“The data are amazing,” said co-author Rafael Fernandes, a theoretical physicist at the University of Minnesota who met senior author Abhay Pasupathy as a postdoc at Columbia. “You can clearly see that there’s a symmetry being broken.”
Broken symmetries often yield novel quantum effects, he explained. Twisted double bilayer graphene usually has three-fold symmetry: no matter how many times you rotate an image of it in 120-degree turns, it stays the same. Using scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy to record the electronic properties of individual atoms, Rubio-Verdú and her colleagues recorded twisted graphene at different voltages. “What we see are stripes,” she said—those are electrons re-aligning and breaking the sample’s symmetry, even as the underlying atomic lattice remains the same. In this observed nematic phase, the image can now only be flipped 180 degrees.
“These phases arise from electron-electron interactions,” said Rubio-Verdú, a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions Fellow who studies electronic phases in moiré materials like twisted graphene with Pasupathy. “Finding a new phase like this one is exciting because it adds to our holistic understanding of graphene-based systems.”
Prior experiments suggested such a correlated electronic phase existed in twisted graphene, but it was unclear whether this was actually the result of strain across the twisted material. Strain can also coax electrons to move around, but this is a mechanical rather than electronic effect, explained Rubio-Verdú. In this experiment, the team used a twisted graphene sample that was relatively large but had extremely low strain—just 0.03 percent. “We’re looking at hundreds of nanometers and the effect persists,” Rubio-Verdú said. “This is an actual electronic nematic phase.”
Theoretically, such a phase could exist in any graphene-based material. In future work, the team plans to explore how the nematic phase influences twisted double bilayer graphene’s capacity to conduct an electrical current.
Understanding the full suite of electronic behavior in moiré materials like twisted graphene may one day help physicists make better sense of another quantum phase, superconductivity, in which an electrical current moves through a material with zero resistance. This phase, however, currently occurs at very low temperatures—even so-called high-temperature superconductors, used in devices like MRI machines, must be kept nearly 100 °F below zero. Although moiré materials like twisted graphene are studied at temperatures nearing -450 °F, they share similarities with high-temperature superconductors, said Rubio-Verdú, like superconducting and insulating states that depend on electron doping.
The field is still asking fundamental questions about the nature of moiré materials, but the discovery of an electronic nematic phase in twisted double bilayer graphene is just one more piece of that puzzle now put into place. “We’re seeing electronic nematicity in another class of compounds,” said Fernandes. “As people are figuring out all kinds of different ways of twisting different layers, we now want to figure out what’s common and robust.”
Read the original article on Columbia University.