This film electrode does not need carbon additives and binders to connect particles like typical slurry-based electrodes, but it still exhibits excellent battery performance. The success of this electrode design provides an efficient strategy for achieving high energy density lithium-ion batteries.
The development of high performance lithium-ion batteries has been highly desirable due to their wide applications in portable electronics and in electric and hybrid vehicles. Silicon is the most promising anode material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries due to its high theoretical specific capacity and safe electrochemical potential. However, Si anode suffers from large volume expansion and contraction during cycling that causes electrical contact loss between silicon and other battery components, eventually leading to battery failure.
Battery researchers from all over the world have been dedicating their efforts to improving Si electrode performance, including researchers at the University of Eastern Finland. Using the electrochemical etching method, they developed a self-standing mesoporous Si film anode for lithium-ion batteries. The idea is that the pores of mesoporous silicon can accommodate the volume expansion during cycling, thus leading to stable battery cycling. They systematically investigated the effects of pore characteristics on electrode performance using correlation analysis and uncovered their relationship.
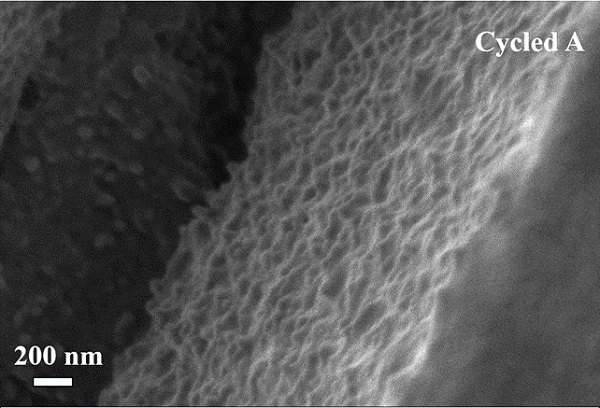
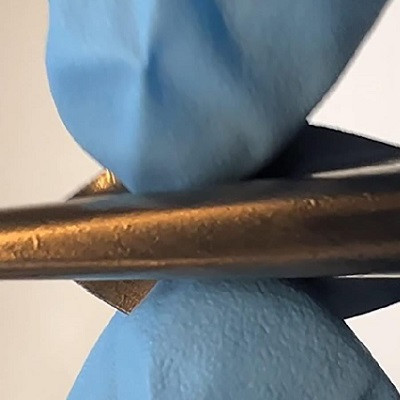
SEM image of the cross-section of the optimal Si film electrode after cycling.
Detailed pore analysis and electrochemical characterization of the Si films were performed to study their correlation. Correlation analysis showed that both reversible specific capacity and initial Coulombic efficiency (ICE) have a strong negative correlation with the porosity and surface area, while the cycling performance is dictated by the film thickness over the pore characteristics. The only positive correlation was found between the long-term cycling stability and the pore diameter. The best Si film anode delivers an ICE of 81.2% and stable cycling for over 450 cycles with a limited specific capacity of 1200 mAh g−1 in half cells.
The study indicates the direction of the porous silicon material for high-performance lithium-ion bateries. More importantly, it provides the researchers in the battery material research, especially Si anode, with a better understanding of the factors involved in evaluating the electrode performance and developing more cost-effective evaluation strategies for battery research.
Read the original article on University of Eastern Finland.