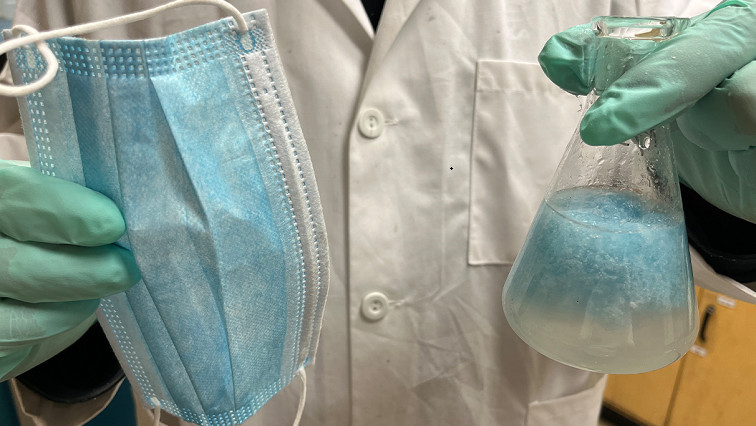
In a paper published in the journal, Materials Letters, a Washington State University research team showed that the mixture using mask materials was 47% stronger than commonly used cement after a month of curing.
“These waste masks actually could be a valuable commodity if you process them properly,” said Xianming Shi, professor and interim chair of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and the corresponding author on the paper. “I’m always looking out for waste streams, and my first reaction is ‘how do I turn that into something usable in concrete or asphalt?’”
Production of cement is a carbon-intensive process, responsible for as much as 8% of carbon emissions worldwide. Microfibers are already sometimes added to cement concrete to strengthen it, but they’re expensive. The microfiber-reinforced concrete can potentially reduce the amount of cement needed for a project or make the concrete last longer, saving carbon emissions as well as money for builders and owners.
Made of a polypropylene or polyester fabric where it contacts the skin and an ultra-fine polypropylene fiber for the filtering layers, medical masks have fibers that can be useful for the concrete industry. If they are not reused, disposable masks can remain in the environment for decades and pose a risk for the ecosystem.
“This work showcases one technology to divert the used masks from the waste stream to a high-value application,” Shi said.
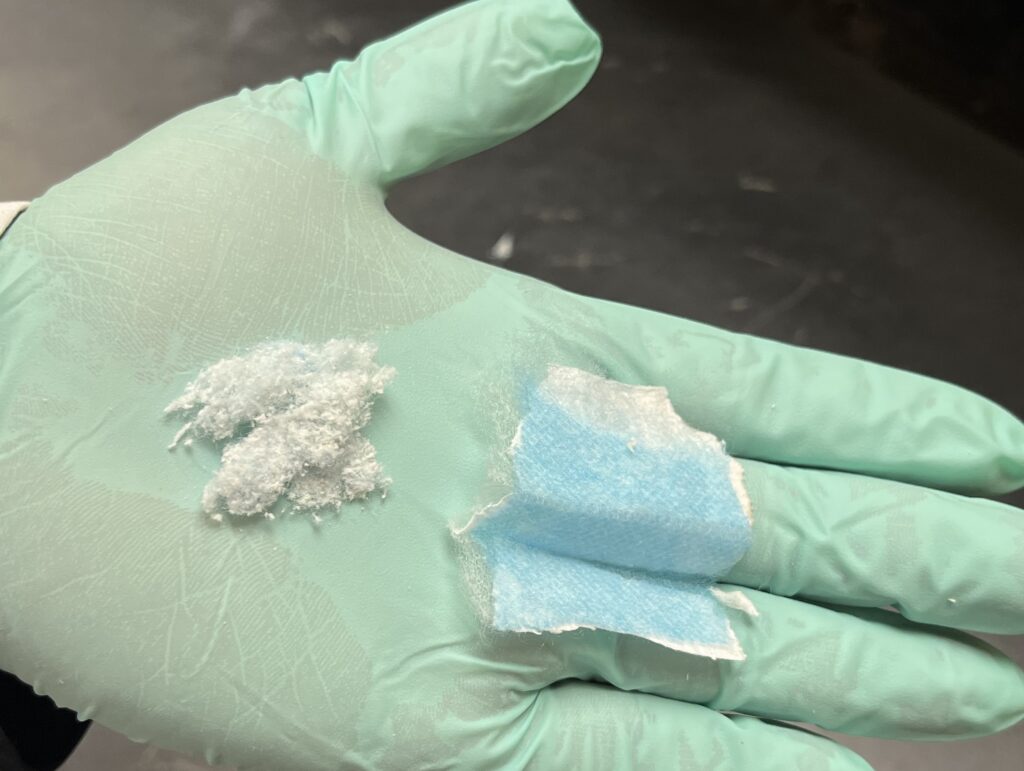

The WSU researchers developed a process to fabricate tiny mask fibers, ranging from five to 30 millimeters in length, and then added them to cement concrete to strengthen it and to prevent its cracking.
In their proof-of-concept work, the researchers developed a process to fabricate tiny mask fibers, ranging from five to 30 millimeters in length, and then added them to cement concrete to strengthen it and to prevent its cracking. For their testing, they removed the metal and cotton loops from the masks, cut them up and incorporated them into ordinary Portland cement, the most common type of cement used around the world and the basic ingredient for concrete, mortar and grout.
They mixed the mask microfibers into a solution of graphene oxide before adding the mixture to cement paste. The graphene oxide provides ultrathin layers that strongly adhere to the fiber surfaces. Such mask microfibers absorb or dissipate the fracture energy that would contribute to tiny cracks in the concrete. Without the fibers, these microscopic cracks would eventually lead to wider cracks and the material’s failure.
The researchers are conducting more studies to test their idea that the graphene oxide-treated microfibers could also improve the durability of the concrete and protect it from frost damage and from deicing chemicals that are used on roadways. They also envision applying this technology to the recycling of other polymer materials, such as discarded clothing, to incentivize the collection of such waste.
Read the original article on Washington State University.