The findings, published in Cell Reports Physical Science, are important because improved carbon capture methods are a key to addressing climate change, said OSU’s Kyriakos Stylianou, who led the study.
Carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, results from burning fossil fuels and is one of the primary causes of a warming climate.
Facilities that filter carbon from the air are beginning to spring up around the globe – the world’s largest opened in 2021 in Iceland – but they’re not ready to make a large dent in the worldwide emissions problem, Stylianou notes. In a year, the Iceland plant can draw out a carbon dioxide amount equivalent to the annual emissions of about 800 cars.
However, technologies for mitigating carbon dioxide at the point of entry into the atmosphere, such as a factory, are comparatively well developed. One of those technologies involves nanomaterials known as metal organic frameworks, or MOFs, that can intercept carbon dioxide molecules through adsorption as flue gases make their way through smokestacks.
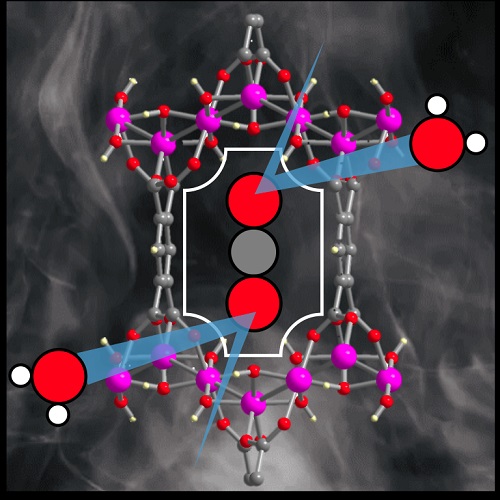
The MOF in question.
“The capture of carbon dioxide is critical for meeting net-zero emission targets,” said Stylianou, who holds the endowed position of Terence Bradshaw Chemistry Professor. “MOFs have shown a lot of promise for carbon capture because of their porosity and their structural versatility, but synthesizing them often means using reagents that are costly both economically and environmentally, such as heavy metal salts and toxic solvents.”
In addition, dealing with the water portion of smokestack gases greatly complicates removing the carbon dioxide, he said. Many MOFs that have shown carbon capture potential lost their effectiveness in humid conditions. Flue gases can be dried, Stylianou said, but that adds significant expense to the carbon dioxide removal process, enough to make it nonviable for industrial applications.
“So we sought to come up with a MOF to address the various limitations of the materials currently used in carbon capture: high cost, poor selectivity for carbon dioxide, low stability in humid conditions, and low CO2 uptake capacities,” he said.
MOFs are crystalline, porous materials made up of positively charged metal ions surrounded by organic “linker” molecules known as ligands. The metal ions make nodes that bind the linkers’ arms to form a repeating structure that looks something like a cage; the structure has nanosized pores that adsorb gases, similar to a sponge.
MOFs can be designed with a variety of components, which determine the MOF’s properties, and there are millions of possible MOFs, Stylianou said. Almost 100,000 of them have been synthesized by chemistry researchers, and the properties of another half-million have been predicted.
“In this study we introduce a MOF composed of aluminum and a readily available ligand, benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylic acid,” Stylianou said. “The synthesis of the MOF happens in water and only takes a couple of hours. And the MOF has pores with a size comparable to that of CO2 molecules, meaning there’s a confined space for incarcerating the carbon dioxide.”
The MOF works well in damp conditions and also prefers carbon dioxide to nitrogen, which is important because nitrogen oxides are an ingredient in flue gasses. Without that selectivity, the MOF would potentially be binding to the wrong molecules.
“This MOF is an outstanding candidate for wet post-combustion carbon capture applications,” Stylianou said. “It’s cost effective with exceptional separation performance and can be regenerated and reused at least three times with comparable uptake capacities.”
Read the original article on Oregon State University.