MXene materials have enormous potential for applications such as energy storage, energy conversion, and electromagnetic shielding due to their excellent physical and chemical properties. M4C3Tx (M = V, Nb, Ta) MXenes have received much attention. However, obtaining a pure MAX phase precursor, complete etching for multi-layer M4C3Tx MXenes, and strict requirements for intercalation agents and exfoliation operations are all difficulties in the synthesis of these few-layer M4C3Tx MXenes. As a result, only a few investigations have focused on the study of thin M4C3Tx (M = V, Nb, Ta) MXenes.
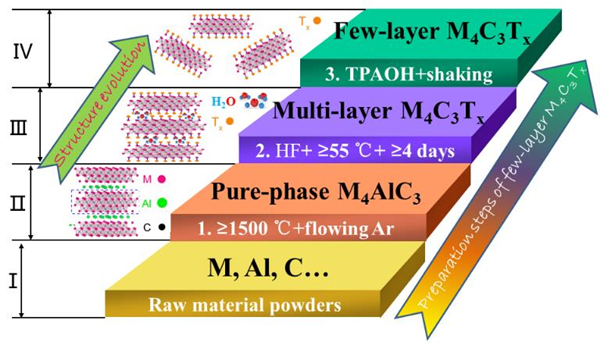
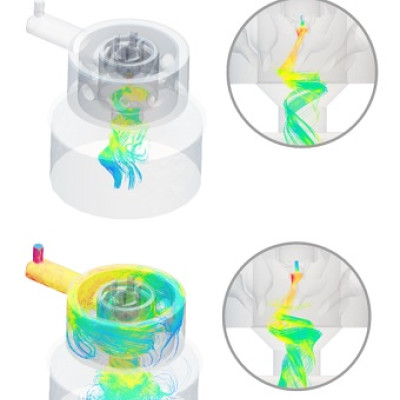
The preparation steps and the corresponding structure evolution of few-layer M4C3Tx (M = V, Nb, Ta) MXenes.
In this study, the scientists proposed a roadmap for the synthesis of defect-free few-layer M4C3Tx (M = V, Nb, Ta) nanosheets. It included high-temperature calcination, HF selective etching, intercalation, and exfoliation. It produced three distinct defect-free few-layer M4C3Tx (M = V, Nb, Ta) nanosheets.
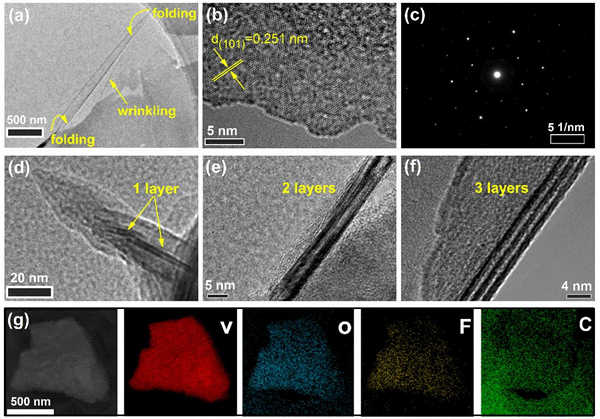
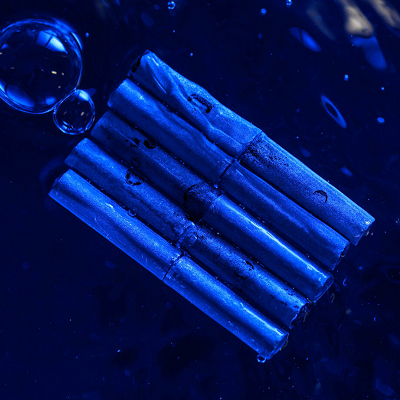
The TEM results of defect-free few-layer V4C3Tx MXene nanosheets.
Extensive characterization confirmed their defect-free structure, significant interlayer spacing (ranging from 1.702 to 1.955 nm), diverse functional groups (-OH, -F, -O), and abundant valence states (M5+, M4+, M3+, M2+, M0).
In addition, they fabricated a free-standing film by vacuum filtration of a few-layer M4C3Tx (M = V, Nb, Ta) MXene ink, which exhibited remarkable physicochemical properties such as high conductivity, high stability, and hydrophilicity.
"Our work provides detailed guidelines for the synthesis of other defect-free few-layer MXene nanosheets," said HUANG Yanan, a member of the team, "and serves as a catalyst for the extensive exploration of functional applications of M4C3Tx (M = V, Nb, Ta) MXene nanosheets in the future."
Read the original article on Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).