The world's reliance on concrete, the second most consumed material after water, is leading to an environmental and resource crisis, with sand mining rates outstripping natural replenishment.
A study by Rice University researchers found that graphene derived from metallurgical coke, a coal-based product, could serve not only as a reinforcing additive in cement but also as a replacement for sand in concrete.
"This could have a major impact on one of the biggest industries in the world," said James Tour, Rice's T. T. and W. F. Chao Professor and a professor of chemistry, materials science and nanoengineering. "We compared concrete made using the graphene aggregate substitute with concrete made using suitable sand aggregates, and we found our concrete is 25% lighter but just as tough."
Concrete, a mixture of aggregates like sand and gravel bonded with cement and water, is essential for urban development. With 68% of the global population expected to live in urban areas by 2050, demand for concrete and hence sand mining is projected to grow significantly. This has tripled in the last two decades, reaching about 50 billion tons yearly. However, this comes at a significant environmental cost.
Cement production, a key component of concrete, accounts for 8% of worldwide carbon dioxide emissions. Moreover, sand mining, largely unregulated, poses severe threats to river and coastal ecosystems. According to a 2022 United Nations report, this escalating demand for sand, coupled with population growth and urban expansion, could soon trigger a "sand crisis."
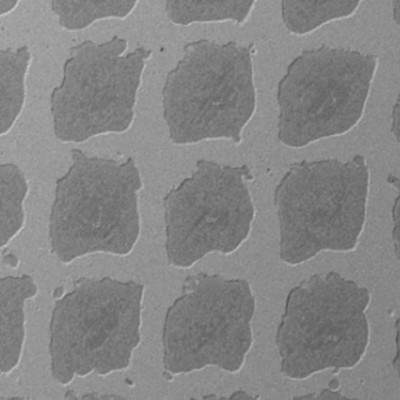
Applying its signature Joule-heating technique to metallurgical coke, the Tour lab has created a type of graphene that could serve as a substitute for sand in concrete.
"Initial experiments where metallurgical coke was converted into graphene resulted in a material that appeared similar in size to sand," said Paul Advincula, a Rice doctoral alum who is a lead author on the study. "We decided to explore the use of metallurgical coke-derived graphene as a total replacement for sand in concrete, and our findings show that it would work really well."
Tests comparing conventional concrete with concrete made from graphene aggregates show promising results. The graphene-based concrete not only matches the mechanical properties of standard concrete but also offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio.
The Tour lab has used Flash Joule heating for a variety of applications, including hybrid carbon nanomaterials synthesis, battery part recycling and heavy metal removal from coal fly ash.
"This technique produces graphene faster and at a larger scale than previous methods," Advincula said.
With the potential to reduce reliance on natural sand and lower carbon emissions from the concrete industry, this new technology could lead to more sustainable urban development practices.
"It will take some time for the price of graphene to get low enough to make this viable," Tour said. "But this just shows there are alternatives we can pursue."
Satish Nagarajaiah, a professor of civil and environmental engineering and of mechanical engineering who is a corresponding author on the study, emphasized that "30% of concrete is composed of sand -- a significant part."
"The fact that we're on the brink of a 'sand crisis' motivates us to look for alternatives, and metallurgical coke, which costs about the same as sand at about 10% of the cost of concrete, could help not only make better-quality concrete, but also eventually translate into significant savings," Nagarajaiah said.
Read the original article on Rice University.