Researchers at Goa University have unlocked a groundbreaking method for producing gold nanoparticles, vital for anti-cancer drug delivery, using a unique species of local mushrooms. This discovery, led by Sujata Dabolkar and scientist Nandakumar Kamat, not only promises to revolutionize the global nanoparticle industry but also aims to boost India's self-reliance in this critical sector.
From Termitomyces to Gold Nanoparticles
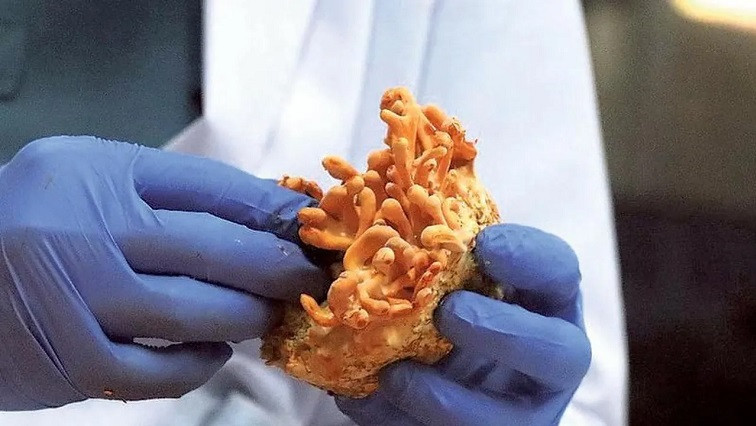
At the core of this innovation is the use of roen almi, a mushroom that grows on termite hills in Goa. The team has developed a technique to cultivate a pure culture of this mushroom in pellet form, which is then utilized to synthesize gold nanoparticles. This method, heralded as the first of its kind globally, offers a sustainable and non-toxic alternative to the chemical processes currently dominating the industry. The implications are significant, not just for the production of gold nanoparticles, valued at 450 million dollars, but also for the preservation of Goa's rich biodiversity.
Local Community and Environmental Impact
The project goes beyond scientific innovation, proposing a unique model for local and global benefits. Kamat and his team have outlined a roadmap that involves local startups in the nanoparticle production process under a revenue and profit-sharing model with the Goa government and local communities. This approach not only taps into the untapped potential of Goa's biodiversity but also aims to ensure the sustainable use of local resources. The conservation of the termitomyces species, some of which face extinction due to overexploitation, is also a key consideration of this groundbreaking project.
Global Significance and Next Steps
The global demand for gold nanoparticles, especially in the medical field for drug delivery systems, is on the rise. The team's research, published in the Geomicrobiology Journal, highlights the potential for India to become a leader in this industry through indigenous methods. The next steps involve engaging with startups and stakeholders to begin production, aiming to create a new ecosystem around gold nanoparticle manufacture that is both economically viable and environmentally sustainable.
The discovery by Goa University's team not only positions India on the map of significant contributors to the global gold nanoparticle industry but also emphasizes the importance of leveraging local biodiversity for technological advancements. As the world moves towards greener alternatives, this indigenous method stands as a beacon of innovation, sustainability, and community engagement.
Read the original article on BNN Breaking.