Led by Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics, the research team recently published a review of the current state of gas-detecting stretchable sensors in Trends in Analytical Chemistry.
Recent developments in gas-sensing technologies have made it possible to detect gaseous biomarkers in humans by monitoring the metabolic process through exhaled breath or skin perspiration and detect harmful or toxic gases in humans’ surrounding environment. Human motions that significantly stretch the skin can degrade or deform the sensors, making it unable to detect gases accurately. To make a more resilient sensor, Cheng and his team investigated the most effective sensor fabrication methods that could work for a variety of applications.
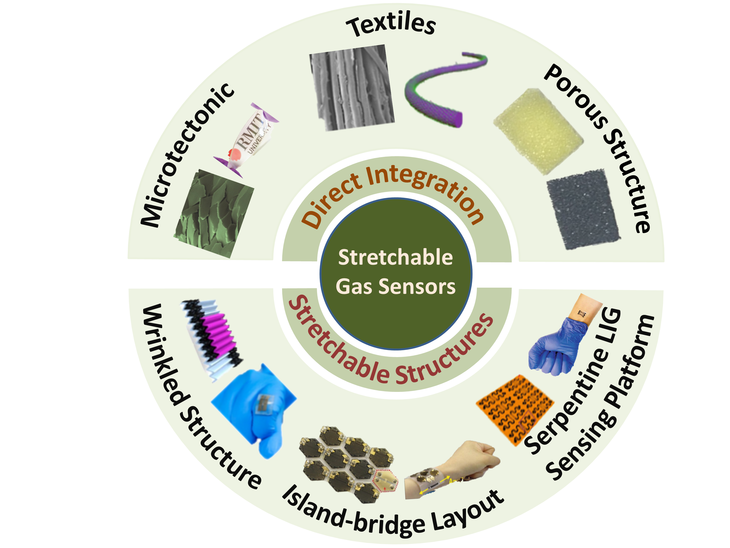
A Penn State research team, led by Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics, is exploring various nanomaterials, sensor designs and fabrication methods that will help in the advancement of stretchable, wearable gas sensors.
“With recent developments in breath analysis, we are starting to build momentum toward developing a gas sensor that could have a larger platform of applications,” Cheng said.
According to Cheng, the gas sensors can help provide an earlier medical diagnosis by detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from human breath, which may indicate the presence of several diseases, including amoebic dysentery, intestinal bacterial infections and cancer. Previous sensors could only monitor glucose and pH levels.
“From human skin perspiration and the exhaled breath, we have about 2,600 biomarkers in the gas form,” Cheng said. “This gives us vital information that we can leverage in the development of disease diagnostics.”
In addition to monitoring these biomarkers, the sensors can detect dangerous levels of toxic gases that may be present in a human’s surrounding environment. For example, the sensors could detect dangerous levels of methane in coal mines and potentially monitor the health and safety of coal miners.
Current gas sensors exhibit similar characteristics to the versions the team is studying, but they have flaws, according to Cheng. For example, metal oxide-based gas sensors have high working temperatures, making them too hot for people to wear. By improving how current gas sensors are fabricated, Cheng said he plans to develop a more reliable and safer gas sensor.
The researchers are specifically interested in a novel platform that directly integrates laser-induced graphene (LIG) via a simple laser scribing process. According to Cheng, this is a cost-effective way to develop a more sensitive, more selective sensor capable of quickly detecting VOCs and harmful gas at ultra-low levels.
LIG is highly porous and can be integrated with carbon-based or metal oxide nanomaterials, which are highly sensitive to gases. Cheng’s platform consists of LIG laser scribed on a film that is transferred to a soft substrate and coated with conductive metal to reduce its resistance. Because of the reduced resistance created through this method, the sensor can easily induce self-heating. The mixed metal oxide integrated with the novel LIG gas-sensing platform makes its workable temperatures significantly lower than the former metal oxide-based gas sensor.
Cheng and his colleagues are also studying how the shapes of composite materials comprising wearable, stretchable gas sensors can affect their environmental sensing performance.
“Though a variety of nanomaterials have been applied for stretchable gas sensors, there is still a wide range of gas-sensitive nanomaterials commonly used in rigid gas sensors that are not explored in their stretchable counterparts,” Cheng said. “We are very interested in exploring these new nanomaterials to provide distinct selectivity, high sensitivity, fast responses and wide detection limits for a new class of stretchable gas sensors.”
The paper was co-authored by Ning Yi, graduate student in materials science and engineering; Mingzhou Shen, graduate student in engineering science and mechanics; and Daniel Erdely, senior engineering science and mechanics student.
Support for this work was provided by the National Science Foundation; the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund; and the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health.
Read the original article on The Pennsylvania State University.