A central section of StatNano website is devoted to indicators. The aim of this section is to monitor global trends, comparing and ranking of countries, organizations and other entities' achievements in the field of nano-science and nanotechnology. Indicators in the database are categorized as (a) general and (b) nano-related ones. Furthermore, these indicators are divided to three main classes according to the measured entities:
- Indicators measured and compared based on countries
- Indicators measured and compared based on universities
- Indicators measured and compared based on nano-materials
Currently, more indicators are measured and compared based on countries in comparison to universities and nano-materials. Almost all general indicators are measured by countries.
Another third classification is adopted based on a chain from scientific achievements to wealth generation. According to this chain, any indicators (regardless of being general or nano-related) falls within one of the following classes:
- Indicators related to Funding and Investment
- Indicators relate to Human Capital
- Indicators related to Scientific achievements
- Indicators related to Innovation (Patents)
- Indicators related to Industry
However, there is a key condition for presenting data for an indicator: If the required data are unavailable for more than 5 countries or date are available for less than 5 continuous time intervals, the corresponding indicators would not be shown in the website, since the main aim is to provide a comprehensive databank for all countries active in the world.
A. General Indicators.
General indicators express general information about countries such as their population and GDP. These indicators are monitored and presented due to the fact that there are "compound" indicators measuring of which is in need of detailed data about general indicators. For instance, "publications per capita" is a compound indicator since if one intends to measure it for a particular country, she requires the population of that country as a general indicator.
General indicators are updated annually based on globally accepted sources such as World Bank and their quantities are extracted after being indexed by the mentioned sources and presented by year and country without any revision or change. Among indicators in this category, the number of ISI indexed articles is dealt with somehow differently with respect to source and methodology. This variation will be explained in what follows. In addition, while patent indicators are general ones as well, the methodology for their measurement will be explained in the nano-related indicators section due to the methodological similarity.
The classification, titles and definitions of general indicators are as follows:
1. Funding & Investment
1.1. Research & development expenditure
- Definition: Expenditures for research and development as current and capital expenditures (both public and private) on creative works undertaken systematically to expand knowledge, including knowledge of nature, humanity, culture, and society, as well as the use of knowledge for new applications. R&D covers basic research, applied research, and experimental development.
- Source: The World Bank
- Unit: Percent (%) of all expenditures
2. Human Capital
2.1. Population
- Definition: All the inhabitants of a particular country.
- Source: The World Bank
- Unit: People
2.2. Researchers active in R&D per million people
- Definition: Researchers active in R&D are professionals engaged in the conception or creation of new knowledge, products, processes, methods, or systems and in the management of the projects concerned. Postgraduate PhD students (ISCED97 level 6) engaged in R&D are included.
- Source: The World Bank
- Unit: People per million people
3. Science
3.1. ISI indexed articles
- Definition: Number of total ISI indexed articles
- Source: Web of Science (ISI Web of Knowledge)
- Unit: Article
- Methodology of measurement:
- Having entered the Web of Science website, the option "Web of Science TM Core Collection" is selected in the "select database" section. In other words, ISI indexed journals are selected.
- Mode of search is "Basic Search".
- Several types of documents are indexed in Web of Science. The selected type from "Document types" menu is "Articles".
- The field for "Topic" is left blank since all articles on any topic are included.
- The year or time interval is determined in "Year Published" menu.
- The name of country (or university/organization) is selected in "Address" menu. Hence, the number of articles related to a country (university/organization) is extracted from its affiliation.
- In the case of finding the number of global articles, the field "Address" is left blank.
- Finally, the "search" button clicked and the required data is extracted.
4. Innovation
4.1. Published patent applications in EPO
- Definition: The indicator shows the number of a particular country's patents applications published (but not yet granted) in EPO. According to WIPO, a patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a product or a process that provides, in general, a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem. To get a patent, technical information about the invention must be disclosed to the public as a patent application.
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
4.2. Published patent applications in USPTO
- Definition: The indicator shows the number of a particular country's patents applications published (but not yet granted) in USPTO. According to WIPO, a patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a product or a process that provides, in general, a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem. To get a patent, technical information about the invention must be disclosed to the public as a patent application.
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
4.3. Total patents in EPO
- Definition: The indicator shows the number of a particular country's granted patents in EPO. According to WIPO, a patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a product or a process that provides, in general, a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem. To get a patent, technical information about the invention must be disclosed to the public as a patent application
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
4.4. Total patents in USPTO
- Definition: The indicator shows the number of a particular country's granted patents in USPTO. According to WIPO, a patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a product or a process that provides, in general, a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem. To get a patent, technical information about the invention must be disclosed to the public as a patent application.
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
5. Industry
5.1 Gross domestic product (GDP)
- Definition: Gross domestic product (GDP) refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given year.
- Source: The World Bank
- Unit: Million US $
5.2. Gross domestic product (PPP)
- Definition: The GDP derived from purchasing power parity (PPP) calculations. Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries.
- Source: The World Bank
- Unit: Million US $
5.3. GDP per Capita (PPP)
- Definition: This indicator consists of a country's GDP on a purchasing power parity basis divided by the population of the country in same year.
- Source: The World Bank
- Unit: US $
B. Nano-related Indicators
Currently, nano-related indicators are confined to categories of Science (Articles), Innovation (Patents), and Industry (Standards). In Science class, a set of indicators are based on the number of articles and measure the quantity of nano-science publications while others are based on the number of citations and measure the quality of scientific achievements. The categories, titles and definitions of general indicators are as follows:
1. Science
I. Indicators of the quantity of nano-related publications
1.1. ISI indexed nano-articles
- Definition: Number of nanotechnology articles indexed in ISI. This indicator is regarded as the simplest and as the same time, the most renowned quantitative indicator for knowledge generation in the field of nano-science.
- Source: Web of Science
- Unit: Article
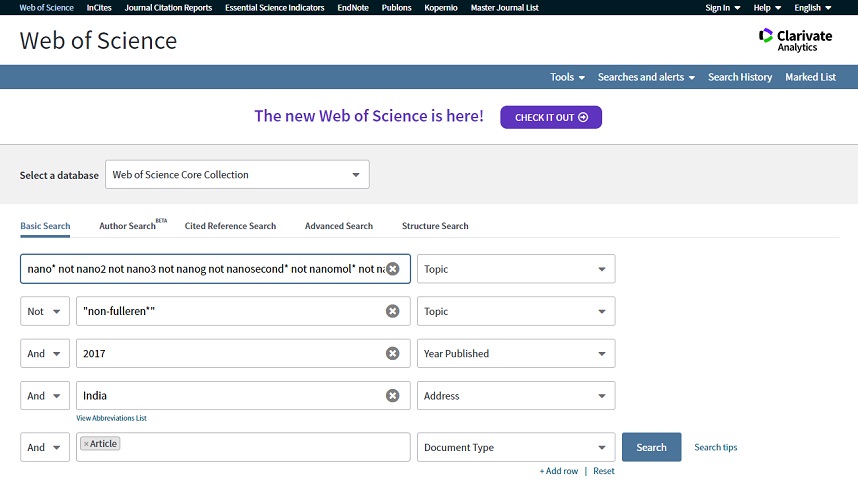
- Methodology of measurement: Given that Web of Science publishes registered journals' articles in all disciplines and scientific fields, it is necessary to provide a specific search string for retrieving nano-articles. This string should be both comprehensive and distinctive so that retrieves nano-articles maximally with the minimum number of non-related articles from other fields. In 2010, a search string was provided and the method of extracting this string has been published in Scientometrics as a paper entitled "A collective and abridged lexical query for delineation of nanotechnology publications". The search string was updated at the end of 2020. The last update constitutes the basis of retrieving nano-article in StatNano:
(nano* not nano2 not nano3 not nanog not nanosecond* not nanomol* not nanogram* not nanoplankton* or "atomic layer deposition*" or "giant magnetoresist*" or superparamagnetism or "single molecule magnet*" or "molecular magnetism" or graphen* or graphyne* or graphane* or dendrimer* or fulleren* or "c-60 layer*" or c60 or buckminsterfulleren* or buckyball* or "bucky-ball*" or "langmuir blodgett*" or mesopor* or "molecul* assembl*" or "molecul* wire*" or "porous silicon*" or "quantum dot*" or "quantum well*" or "quantum comput*" or "quantum wire*" or qubit* or "self assembl*" or supramolecul* or supermolecul* or "ultrathin film*" or "ultra-thin film*" or "carbon dot*" or "carbonized polymer dot*" or borophen* or mxene* or phosphorene* or "blue phosphorus" or ("virus like particle*" not chimeric) or "metal organic framework*" or "molecular switch*" or "single molecule switch*" or "single molecule electronic*" or "molecular electronic*" or germanene or silicene or ("Molybdenum disulfide" and (monolayer* or "few layer*" 2D or "two dimension*")))
Next box (Topic) : NOT "non-fulleren*"
Next steps for retrieving nano-articles are described in the following:
- Having entered the Web of Science, the option "Web of Science TM Core Collection" is selected in the "select database" section. In other words, ISI indexed journals are selected.
- Mode of search is "Basic Search"
- Several types of documents are indexed in Web of Science. The selected type from "Document types" menu is "Articles".
- The abovementioned search string is selected for "Topic" field. The search is undertaken by Title, Abstract and Keywords.
- The year or time interval is selected in "Year Published" menu.
- The name of country (or university/organization) is selected in "Address" menu. Hence, the number of articles related to a country (university/organization) is extracted from its affiliation.
- In the case of finding the number of global nano-articles, the field "Address" is left blank. It is worthy to mention that one cannot add countries' nano-articles to reach the global publications since there are several overlaps among different countries' nano-articles. In other words, the sum of all countries' nano-articles would be much more than the real global publications.
- Finally, the "search" button clicked and the required data is extracted.
1.2. Local share in nanoscience
- Definition: A country/organization's ISI-indexed nano-articles divided by its total ISI-indexed articles. This indicator represents the ratio of a particular country/organization's nano-articles to its total scientific articles in a given period. The indicator is regarded as a measure for national/organizational priority of nanoscience.
- Source: Web of Science (ISI Web of Knowledge)
- Unit: Percent
1.3. National priority of nanoscience
- Definition: This indicator is considered as another measure for national priority of nanoscience as well and shows a particular country's concentration on scientific activities in the field of nano-science. Four quantities are needed for calculating this indicator: the number of a country' total ISI-indexed articles (CT), the number of a country' nano-articles (CN), the number of global ISI-indexed articles (WT), and the number of global nano-articles (WN): The share of a country's nano-articles from its total scientific publications divided by the share of the global nano-articles from global publications i.e. (CN/CT)/(WN/WT)
- Source: Web of Science (ISI Web of Knowledge)
- Unit: -
1.4. The number of nano-articles per GDP (PPP)
- Definition: The number of a country's nano-articles divided by its GDP (PPP) in billion $. This indicator is a measure of relative expenditure for providing a nano-article in a given country.
- Source: Web of Science, the World Bank
- Unit: Article per billion $
1.5. The number of nano-articles per population
- Definition: The number of a country's nano-articles divided by its population in million people. This indicator is a measure of nano-scientific achievements per capita for a given country.
- Source: Web of Science, the World Bank
- Unit: Article per million people
1.6. The share of international collaboration in nano-science
- Definition: The number of a particular country's nano-articles with authors of two or more countries divided by total number of the country's nano-articles. This indicator is a measure of the level of international collaboration among scientists of a given country who are active in nano-science publications.
- Source: Web of Science, The World Bank
- Unit: Percent
-
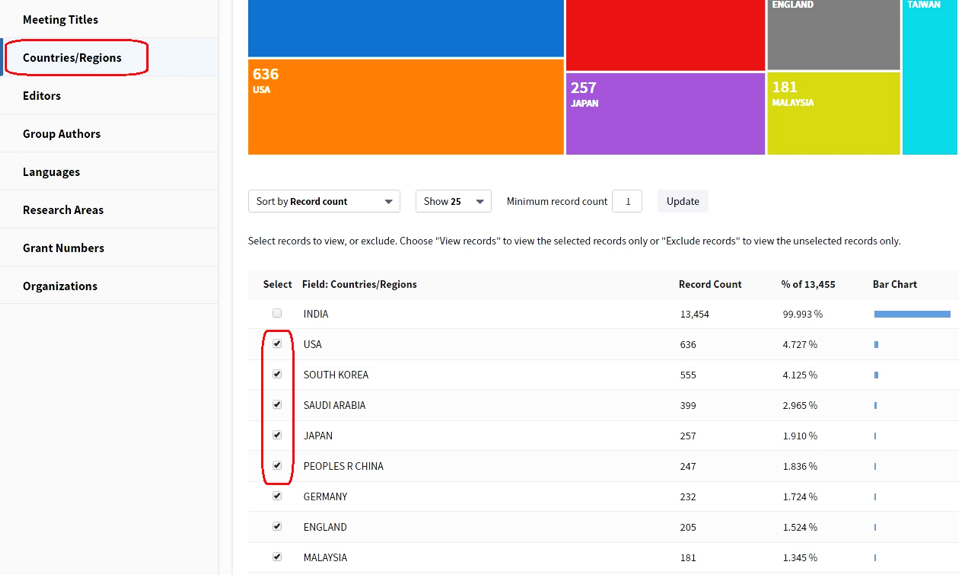
Methodology of measurement: First of all, a given country's nano-articles are retrieved according the methodology described earlier (indicator 1.1). Then, the option "Analyze Result" is employed in order to determine the level of collaborations. If one selects the "Countries/Regions" option, the number of found articles will be shown by countries. For identifying a given country's joint articles (i.e. articles with authors from two or more countries), all countries except the considered one are selected. Then, by clicking "View Records" button, the number of joint articles will be shown. Finally, the indicator is calculated by dividing the mentioned number to the number of nano-articles published by the considered country. The average global share of international collaboration consists of numerical average of this indicator calculated for each country.
The below picture shows the "Countries/Region" page in Web of Science website.
It is noticeable that one cannot use the sum of all countries' nano-articles in order to calculate the number of joint articles. Given that joint articles are enumerated twice or more (according to the number of authors form different countries), the sum of countries' nano-articles is always more than the real number of global nano-articles. By clicking "View Records" option, each unique article is enumerated just one time and the mentioned problem will be avoided.
II. Indicators of the quality of nano-related publications
1.7. Total number of nano-articles' citations
- Definition: The number of citations to nano-articles published by a given country. It is evident that the number of publications and related indicators do not give us a reliable perspective about to which extent such publications are studied by other scholars and whether they have influence on future research or not. The indicators in this category tries to provide measures of the quality of nano-articles.
- Source: Web of Science
- Unit: Citations
-
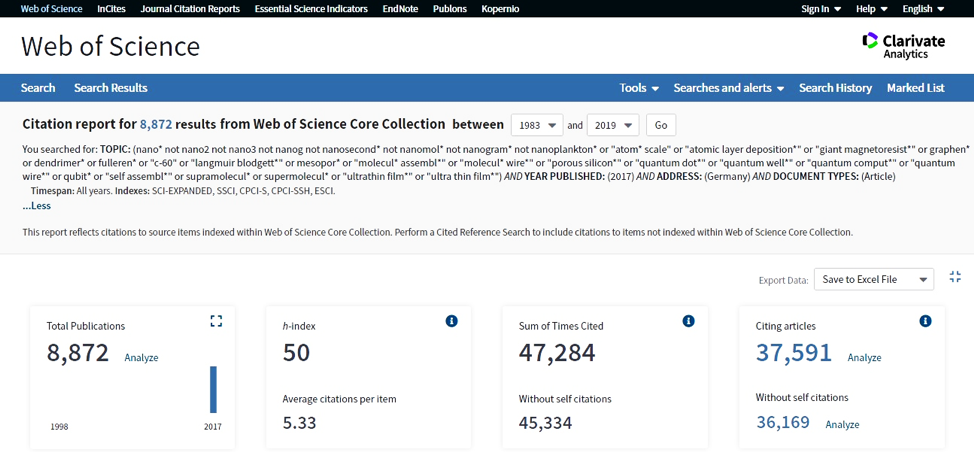
Methodology of measurement: Firstly, indexed nano-articles by a particular country are retrieved as it is described earlier. Then, the option "Create Citation Report" is selected and the number of citation can be reached by clicking the "Sum of the Times Cited" button. The shown number is the total number of all citations to the selected articles from the time of their publication. Obviously, more recent articles have typically less citations due to shorter time span after publication. The below picture shows this section in Web of Science website.
An important point here is that if the number of selected articles amounts to 10,000, the option "Create Citation Report" will become inactive. In such cases, on has to break the selected articles by year of publication, journals, universities etc. and analyze them in groups with less than 10,000 articles.
1.8. h-Index of nano-articles
- Definition: The number of citations to nano-articles published by a given country. It is evident that the number of publications and related indicators do not give us a reliable perspective about to which extent such publications are studied by other scholars and whether they have influence on future research or not. The indicators in this category tries to provide measures of the quality of nano-articles.
- Source: Web of Science
- Unit: Citations
-
Methodology of measurement: Firstly, indexed nano-articles by a particular country are retrieved as it is described earlier. Then, the option "Create Citation Report" is selected and the number of citation can be reached by clicking the "Sum of the Times Cited" button. The shown number is the total number of all citations to the selected articles from the time of their publication. Obviously, more recent articles have typically less citations due to shorter time span after publication. The below picture shows this section in Web of Science website.
An important point here is that if the number of selected articles amounts to 10,000, the option "Create Citation Report" will become inactive. In such cases, on has to break the selected articles by year of publication, journals, universities etc. and analyze them in groups with less than 10,000 articles.
1.9. Average citation per nano-article
- Definition: The number of a country's total citations divided by the number of nano-articles.
- Source: Web of Science
- Unit: Citation
- Methodology of measurement: Having the number of a particular country's nano-article and the total number of their citations (Indicators 1.1 and 2.1 above) at hand, the quantity of this indicator can be calculated directly. The "Five year average citation per nano-article" is defined similarly but this indictor is measured just for a 5 year period.
Indicators 1.1, 1.7, 1.8, and 1.9 can be measured for universities and research organizations as well. For retrieving a particular university/organization's articles, its name is selected in "Address" section. A relatively same method is used for finding articles about specific nano-material, but the proper search string for the nano-material is written in the "Topic" field as it is shown in the below picture. A detailed methodology is described in the methodology section for "Nano-material Databank"
2. Innovation
The main indicator in this section is the number of patents registered in well-known patent offices. Currently, patents registered in United Sates Patent and Trademark office (USPTO) and European Patent Office (EPO) are studied in Innovation section. The required data are extracted form Orbit database which is one of the most comprehensive databases in the field with powerful search engine and considerable analysis services. Information about more than 30 patent offices throughout the world is published in Orbit database.
Patent registration documents are classified in two main categories: finalized or "granted patents" and "published patent applications". The second class are applications which are published after peer review but are not totally approved yet. Indicators for both categories are defined and measured in StatNano database.
2.1. Nanotechnology patents in EPO
- Definition: This indictor shows the number of nanotechnology granted patent in EPO. According to ISO/TS 18110 (First Edition 2015-08-15), the definition of nanotechnology patents is as “patents that include at least one claim related to nanotechnology or patents classified with an IPC classification code related to nanotechnology such as B82."
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
2.2. Nanotechnology published patent applications in EPO
- Definition: This indictor shows the number of nanotechnology published patent applications (but not yet granted) in EPO.According to ISO/TS 18110 (First Edition 2015-08-15), the definition of nanotechnology patents is as “patents that include at least one claim related to nanotechnology or patents classified with an IPC classification code related to nanotechnology such as B82."
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
2.3. Nanotechnology patents in USPTO
- Definition: This indictor shows the number of nanotechnology granted patent in USPTO. According to ISO/TS 18110 (First Edition 2015-08-15), the definition of nanotechnology patents is as “patents that include at least one claim related to nanotechnology or patents classified with an IPC classification code related to nanotechnology such as B82."
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
2.4. Nanotechnology published patent applications in USPTO
- Definition: This indictor shows the number of nanotechnology published patent applications (but not yet granted) in USPTO. According to ISO/TS 18110 (First Edition 2015-08-15), the definition of nanotechnology patents is as “patents that include at least one claim related to nanotechnology or patents classified with an IPC classification code related to nanotechnology such as B82."
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Patent
2.5. The share of nanotechnology patents to total patents
- Definition: The indicator shows the share of nanotechnology patents to total patents registered either in USPTO or EPO (share of nano to total).
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Percent
2.6. The share of nanotechnology patent applications to total patent applications
- Definition: The indicator shows the share of nanotechnology published patent applications to total published patent applications registered in either USPTO or EPO (share of nano to total)
- Source: Orbit.com
- Unit: Percent
2.7. Ratio of nanotechnology patents to nano-articles
- Definition: The number of a country's nanotechnology granted or published patents registered either in UPSTO or EPO per 100 ISI nano-articles published by the country in the same year. This indicator is a measure for comparing intensity of a country's achievement in nano-science and in nanotechnology innovations
- Source: Web of Science, Orbit.com
- Unit: Patents per 100 articles
2.8. Methodology of measuring innovation indicators
StatNano makes use of Orbit database for extracting raw or analyzed data about patents. The data are retrieved based on full text search by three main classes of granted patents and published patent applications.
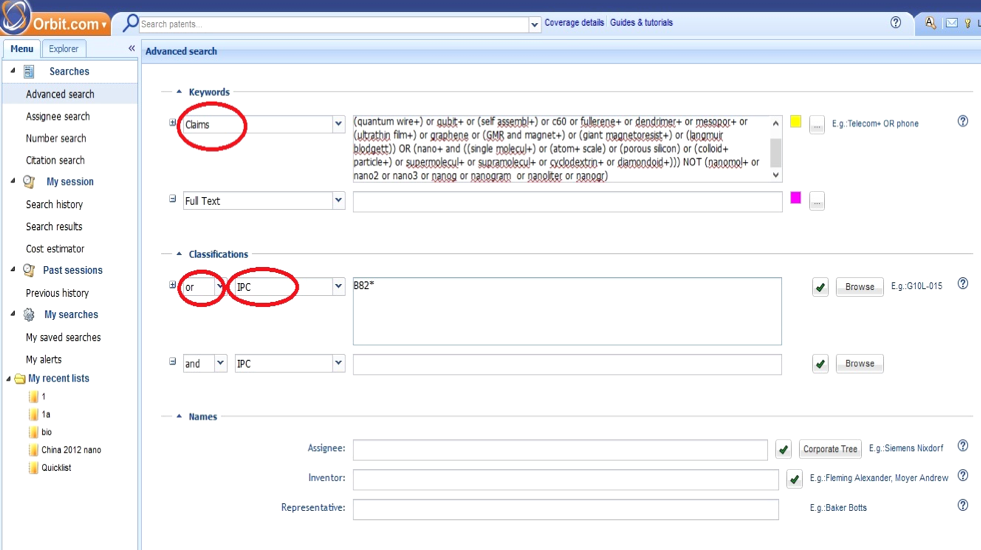
First of all, the type of document (grant or published application) is determined. Then the abovementioned search string is utilized for identifying nanotechnology related patents. This string has been redefined according to Orbit data operators as what follows:
(((nano+ not nanosecond+) or (quantum dot+) or (quantum comput+) or (quantum 1d well+) or (quantum wire+) or qubit+ or (self assembl+) or c60 or fullerene+ or dendrimer+ or mesopor+ or (ultrathin film+) or graphene or (GMR and magnet+) or (giant magnetoresist+) or (langmuir blodgett)) OR (nano+ and ((single molecul+) or (atom+ scale) or (porous silicon) or (colloid+ particle+) or supermolecul+ or supramolecul+ or cyclodextrin+ or diamondoid+))) NOT (nanomol+ or nano2 or nano3 or nanog or nanogram or nanoliter or nanogr)
The search based on the string is undertaken for "Patent Claims". Furthermore, according the definition of nanotechnology patents, every patent that is classified under code B82 according to International Patent Classification (IPC) is added to the search results.
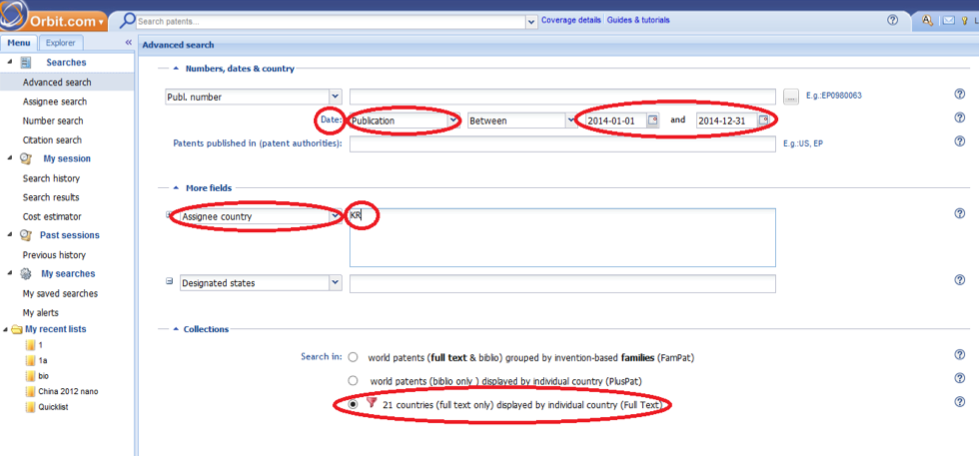
The time of publication is determined based on publication date which can be retrieved form "Date" section on Orbit webpages.
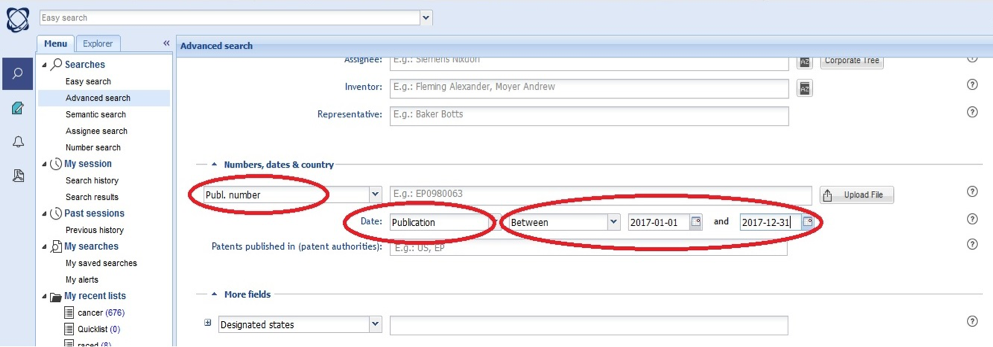
All countries which are registered as a patent's assignee are mentioned in the corresponding field. Hence, a given patent may be enumerated for more than on country (as it is the case for nan-articles). At the time of searching, the abbreviation for a particular country (such as KR for South Korea) is selected in "Assignee Country" in "More Fields" section. The following pictures show this process:
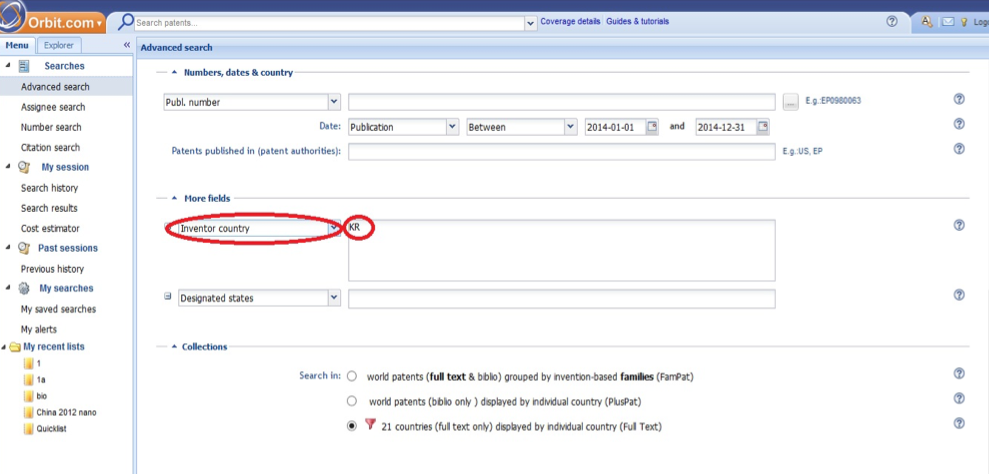
Sometimes, the assignee field has been left blank for a patent. In such cases, inventors are considered and the corresponding countries are regarded as relevant assignees. So, the abbreviation for a particular country (such as KR for South Korea) is selected in "Inventor Country" in "More Fields" section (See the below picture). Then, the search result with blank assignee are enumerated and the resultant quantity will be added to the result of search by assignee. This sum constitutes the number of patents for a given country.
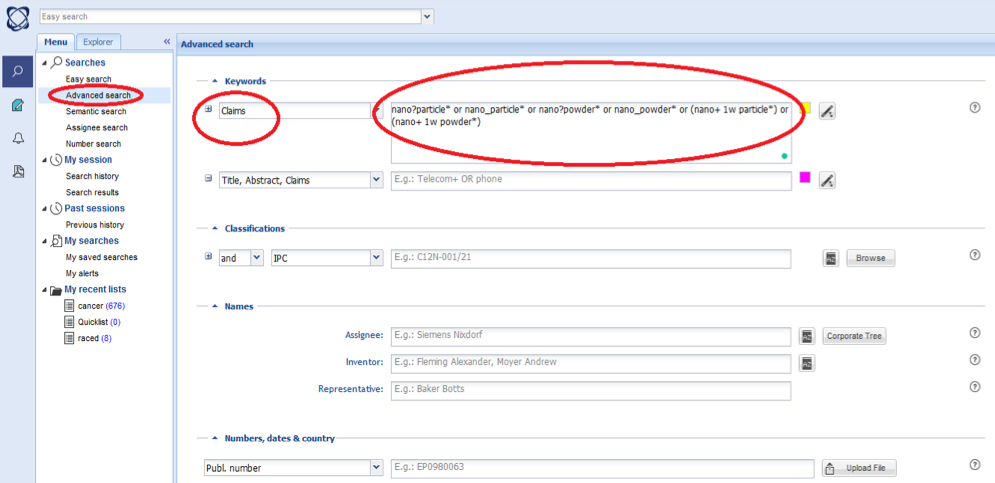
Among Innovation indicators, USPTO granted patents and published patent applications (indicators, 2.3 and 2.4) are also measured by nano-material. The search method is overally similar to search procedure for nanotechnology patents but specific search strings are used for nano-materials in "Advanced Search" section. According to definition of nanotechnology patents (ISO/TS 18110 first edition 2015-08-15), the search based on specific strings are undertaken just in "Claim" section of patent documents.
Currently, 44 nano-materials have been defined in StatNano and their search string are included in the following table:
|
No. |
Nanomaterial/nanostructure |
Search String |
|
1 |
Nanoparticles |
nano?particle* or nano_particle* or nano?powder* or nano_powder* or (nano+ 1w particle*) or (nano+ 1w powder*) |
|
2 |
Nanocrystallines |
(Nano?crystal*) or (nano-crystal*) or (crystallin* 1D nanoparticle*) |
|
3 |
Nanotubes |
(NANOTUB* OR "NANO-TUB*" OR SWCNT* OR MWCNT* OR (NANO* 1W TUB*) or (CNT F nano*) or (CNT F layer*) or (CNT F film*) or (CNT F grapheme*) or (CNT S dispersion liquid) or (CNT S sheet*) or (CNT F carbon*) or (CNT F yarn*) or (CNT F angstrom*) or (CNT F catalyst*) or (CNT F powder*) or (CNT F composit*)) |
|
4 |
Nanoporous materials |
Nano?porous* or nano-porous* or (nono* 1d porous*) or (mesopor*) or (meso pore*) or (meso#por*) |
|
5 |
Porous silicon |
(Porous* silicon*) or (porous* 1d silicon*) |
|
6 |
Nanofoams |
(nano 1d foam) or (nanofoam*) or (nano-foam*) |
|
7 |
Aerogels |
(aerogel*) or (nanoaerogel*) |
|
8 |
Nanopores |
(nanopore* or nano-pore* or nanohole* or nano-hole* or(nano 1w pore*) or (nano 1w hole*)) |
|
9 |
Quantum dots |
(quantum* 1D dot*) |
|
10 |
Nanocomposites |
nanocomposite* or "nano-composite*" or (nano?composite*) or (nano* S composite*) |
|
11 |
Quantum wells |
quantum* 1D well* |
|
12 |
Super molecules |
(super_molecule*) or (supra_molecule*) |
|
13 |
Nanocolloids |
(colloid* particle*) or (nanocolloid) or (nano-colloid*) or (coloid* 1w particle*) or (nano 1w colloid) |
|
14 |
Nanofluids |
nanofluid or nano-fluid or nanofluids or nano-fluids or (nano 1w fluid) or (nano 1w fluids) |
|
15 |
Nanofluidic |
(nanofluidic* or nano-fluidic* or (nano 1d fluidic*)) |
|
16 |
Nanowires |
(nanowire*) or (nano-wire*) or (molecul* wire*) or (nano* 1D wire*) or (molecul* 1D wire*) |
|
17 |
Quantum Wires |
(quantum wire*) or (quantum * 1D wire*) or (quantum string*) |
|
18 |
Self-assembled Layers |
(self-assembl* layer*) or (self-assembl* monolayer*) or (self-assembl* multilayer*) or (self-assembl* mono-layer*) or (self-assembl* multi-layer*) or (self-assembl* 1d layer*) or (self-assembl* 1w monolayer*) or (self-assembl* 1w multilayer*) or (self-assembl* 1w mono-layer*) or (self-assembl* 1w multi-layer*) |
|
19 |
Langmuir Blodget |
(langmuir* blodget*) or (langmuir* 1w blodget*) |
|
20 |
Nanolayers |
(nanolayer*) or (nano-layer*) |
|
21 |
Nanoflims |
(ultrathin film*) or (ultra-thin film*) or (nanofilm*) or (nano-film*) or (ultrathin 1w film*) or (ultra-thin 1w film*) |
|
22 |
Nanocoatings |
(nanocoat*) or (nano-coat*) |
|
23 |
Fullerenes |
(buckybal* or c-60 or c-70 or ful?erene*) |
|
24 |
Quantum Computers |
(quantum 1D comput*) or (qubit*) or (quantum 1W processo*) or (Quantum 1D Machine) |
|
25 |
Dendrimers |
Dend?rime* |
|
26 |
Nanofibers |
(nano* 1D fiber*) or (nano* 2w fiber*) or (nano* 1D fibre*) or (nano* 2w fibre*) or (nanofiber*) or (nanofibre*) or (nano* 2D yarn*) or (nanofilament*) or (nano-filament*) or (nanofibril*) or (nano-fibril*) |
|
27 |
Nanocapsules |
(nano* 1w capsule*) or (nanocapsule*) or (nano-capsule*) |
|
28 |
Nanoshells |
(nanoshell*) or (nano-shell*) or (nano* shell*) or (nano-core-shel*) or (nanocore-shel*) or (nano core shel*) |
|
29 |
Nanoliposomes |
(nano-liposome*) or (nanoliposome*) or (nano liposome*) |
|
30 |
Nanomicelle |
nanomicelle* |
|
31 |
Graphene |
graphen* |
|
32 |
Graphyn |
graphyn* |
|
33 |
Borophen |
Borophen* |
|
34 |
Nanorodes |
(nano?rod*) or (Nano* 1D rod*) |
|
35 |
Nanospheres |
(nano?spher*) or (Nano* 1D spher*) |
|
36 |
Nanoclusters |
(nano?cluster*) or (Nano* 1D cluster*) |
|
37 |
Nanoribbons |
(nano?ribbon*) or (Nano* 1D ribbon*) or (nano?tape*) or (Nano* tape) |
|
38 |
Nanosheets |
nanosheet* or (nano* 1W sheet*) or nanoplate* or (nano* 1W plate*) or (nanfoil* or nano-foil* or nanoflake* or nano-flake*) |
|
39 |
Nanoelectromechanical Systems |
((nanoelectromechanic* system*) or (nano-electromechanic* system*) or (nano* 1W electromechanic* 1W system*) or (NEMS)) |
|
40 |
Nanoonions |
nanoonion* or (nano-onion*) or nano* onion* |
|
41 |
Nanohorns |
(nanohorn* or nano-horn* or (nano* 2w horn*)) |
|
42 |
Nanostars |
(nanostar* or nano-star* or (nano* star) or (nano 1w star)) |
|
43 |
Diamondiod |
(diamondoid* or nanodiamond* or nano-diamond* or (nano 1d diamond*)) |
|
44 |
Nanolayers-Nanofilms |
(nanolayer*) or (nano-layer*) or (ultrathin film*) or (ultra-thin film*) or (nanofilm*) or (nano-film*) or (ultrathin 1w film*) or (ultra-thin 1w film*) or (nanocoat*) or (nano-coat*) |
In the "Keyword" section, the "Claims" option is selected from left bar and the search string is written in the right cell as it is shown in the below picture.
The date for searching is patents' publication date. This element is entered in the "Date" section. For example in the following picture, the patents published in 2017 would be retrieved by entering date between 2017-01-01 and 2017-12-31. All search are undertaken in "Full Text" section.
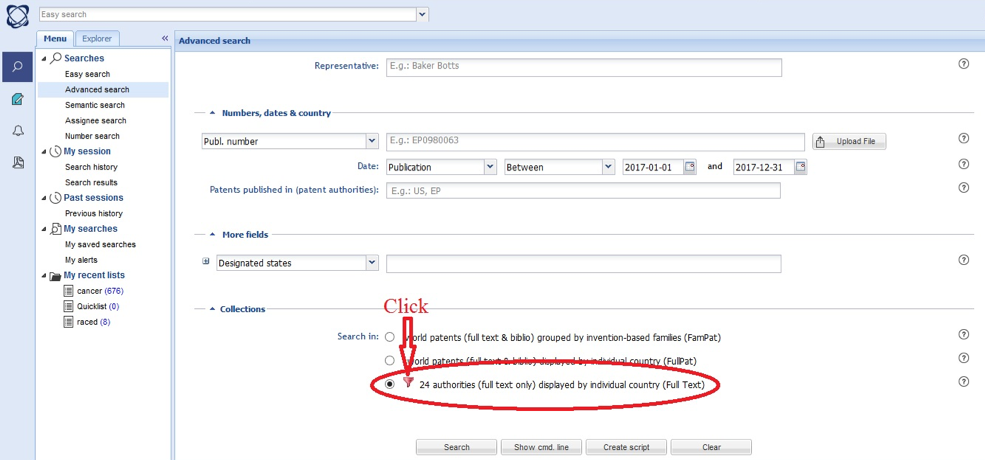
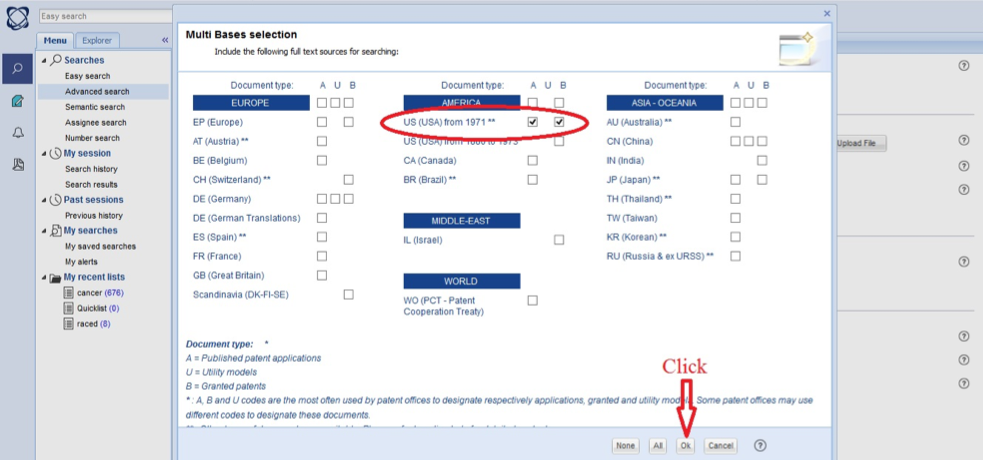
After clicking the "Full text" option (see picture above), the user can select patent office(s). For each office, it is possible to select granted patents (column B) and/or published patent applications (column A). After selecting type of document, one has to click "Ok" button to save changes (see the below picture).
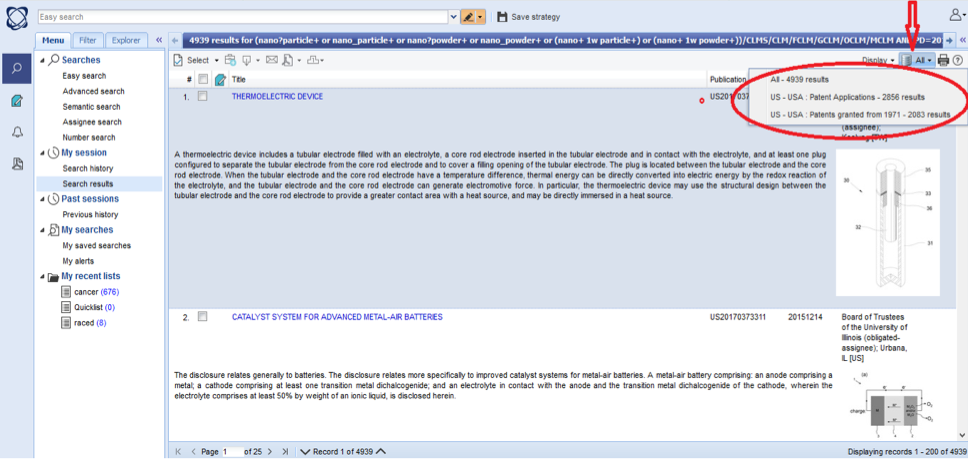
After saving setting and clicking "Search" button, one can classify the result by the type of document and by patent office by clicking "All" button as it is shown in the following picture.
3. Industry
In the industry section, the only nano-related indicator is the number of national standards and other indicators in this section are general ones. Several other indicators such as the number of products, active companies and the market value can be defined in this section, nevertheless, these indicators are not measured currently due to lack of international reliable database and comparable data for different countries. However, the product databank is designed as a separate section of StatNano website for monitoring commercialization and applications of nanotechnology. Detailed information about this databank can be found in the related section of the website.
3.1. The number of national nanotechnology standards
-
Definition: Standard is a document, established by consensus and approved by a recognized body that provides, for common and repeated use, rules, guidelines or characteristics for activities or their results, aimed at the achievement of the optimum degree of order in a given context.
National nanotechnology standard is a nanotechnology related standard that is adopted by a national standards body and made available to the public.
- Source: StatNano Databank
- Unit: Standard
-
Methodology of measurement: Nanotechnology standards are found and extracted using a set of keywords related to this field. The main sources are websites of national and international organizations responsible for developing and issuing standards. In addition, other sources such as analytic reports and websites for standards' sale are monitored for finding new standards, however the crucial criterion for a standard to be recorded in the database is the accessibility of its information in the website of official corresponding organization. National standard organizations in countries which are members or observers of ISO/TC 229 are monitored continually. Moreover, standardization activities of countries which have national plans or roadmaps in the field of nanotechnology are considered periodically.
So, any national or international standard whose information is accessible in the responsible organization website in English language and keywords related to nanotechnology have been cited in its title and/or abstract will be recorded in the database.
The registered standards are retrieved dynamically from the databank and shown by date and country. More information about standard databank can be found in the related section in the StatNano website.