

| Date | 25th, May 2018 |
|---|
Home > Press > Switching with molecules: Molecular switch will facilitate the development of pioneering electro-optical devices
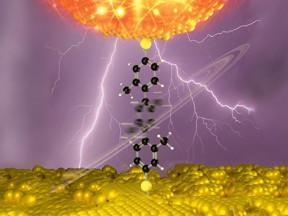 A research team at the Technical University of Munich has developed molecular nanoswitches that can be toggled between two structurally different states using an applied voltage. They can serve as the basis for a pioneering class of devices that could replace silicon-based components with organic molecules.
CREDIT
Yuxiang Gong / TUM / Journal of the American Chemical Society
A research team at the Technical University of Munich has developed molecular nanoswitches that can be toggled between two structurally different states using an applied voltage. They can serve as the basis for a pioneering class of devices that could replace silicon-based components with organic molecules.
CREDIT
Yuxiang Gong / TUM / Journal of the American Chemical Society
Abstract: A research team led by physicists at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has developed molecular nanoswitches that can be toggled between two structurally different states using an applied voltage. They can serve as the basis for a pioneering class of devices that could replace silicon-based components with organic molecules.
Munich, Germany | Posted on May 25th, 2018
The development of new electronic technologies drives the incessant reduction of functional component sizes. In the context of an international collaborative effort, a team of physicists at the Technical University of Munich has successfully deployed a single molecule as a switching element for light signals.
"Switching with just a single molecule brings future electronics one step closer to the ultimate limit of miniaturization," says nanoscientist Joachim Reichert from the Physics Department of the Technical University of Munich.
Different structure - different optical properties
The team initially developed a method that allowed them to create precise electrical contacts with molecules in strong optical fields and to control them using an applied voltage. At a potential difference of around one volt, the molecule changes its structure: It becomes flat, conductive and scatters light.
This optical behavior, which differs depending on the structure of the molecule, is quite exciting for the researchers because the scattering activity - Raman scattering, in this case - can be both observed and, at the same time, switched on and off via an applied voltage.
Challenging technology
The researchers used molecules synthesized by teams based in Basel and Karlsruhe. The molecules can change their structure in specific ways when they are charged. They are arranged on a metal surface and contacted using the corner of a glass fragment with a very thin metal coating as a tip..
This serves as an electrical contact, light source and light collector, all in one. The researchers used the fragment to direct laser light to the molecule and measure tiny spectroscopic signals that vary with the applied voltage.
Contacting individual molecules electrically is extremely challenging from a technical point of view. The scientists have now successfully combined this procedure with single-molecule spectroscopy, allowing them to observe even the smallest structural changes in molecules with great precision.
Competition for Silicon
One goal of molecular electronics is to develop novel devices that can replace traditional silicon-based components using integrated and directly controllable molecules.
Thanks to its tiny dimensions, this nanosystem is suitable for applications in optoelectronics, in which light needs to be switched using variations in electrical potential.
###
The research project was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) for the Cluster of Excellence Munich-Centre for Advanced Photonics (MAP) and SPP 1243, as well as the Eropean Union (ERC Advanced Grant MolArt and FET Measure 2D-ink).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Andreas Battenberg
49-892-891-0510
Copyright © Technical University of Munich (TUM)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Organic Electronics
![]() Flexing the power of a conductive polymer: A new material holds promise for the next generation of organic electronics June 24th, 2022
Flexing the power of a conductive polymer: A new material holds promise for the next generation of organic electronics June 24th, 2022
![]() 'Fruitcake' structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
'Fruitcake' structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
Hardware
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
![]() Do you Kyoto? World-leading companies share their approaches to environmentally friendly business at NAUM'19 October 14th, 2019
Do you Kyoto? World-leading companies share their approaches to environmentally friendly business at NAUM'19 October 14th, 2019
Possible Futures
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() Deep-ultraviolet nonlinear optical crystals: Concept development and materials discovery July 8th, 2022
Deep-ultraviolet nonlinear optical crystals: Concept development and materials discovery July 8th, 2022
![]() Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes July 8th, 2022
Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes July 8th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() 'Life-like' lasers can self-organise, adapt their structure, and cooperate July 15th, 2022
'Life-like' lasers can self-organise, adapt their structure, and cooperate July 15th, 2022
![]() Electrically driven single microwire-based single-mode microlaser July 8th, 2022
Electrically driven single microwire-based single-mode microlaser July 8th, 2022
![]() Deep-ultraviolet nonlinear optical crystals: Concept development and materials discovery July 8th, 2022
Deep-ultraviolet nonlinear optical crystals: Concept development and materials discovery July 8th, 2022
