

| Date | 12th, Jan 2019 |
|---|
Home > Press > Chemical synthesis of nanotubes: Nanometer-sized tubes made from simple benzene molecules
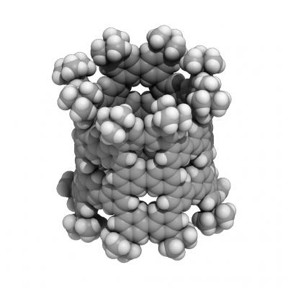 A nanometer-sized pNT cylinder made of 40 benzenes. The cylinder is tens of thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
CREDIT
(c)2018 Hiroyuki Isobe
A nanometer-sized pNT cylinder made of 40 benzenes. The cylinder is tens of thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
CREDIT
(c)2018 Hiroyuki Isobe
Abstract: For the first time, researchers used benzene - a common hydrocarbon - to create a novel kind of molecular nanotube, which could lead to new nanocarbon-based semiconductor applications.
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on January 11th, 2019
Researchers from the Department of Chemistry have been hard at work in their recently renovated lab in the University of Tokyo's Graduate School of Science. The pristine environment and smart layout affords them ample opportunities for exciting experiments. Professor Hiroyuki Isobe and colleagues share an appreciation for "beautiful" molecular structures and created something that is not only beautiful but is also a first for chemistry.
Their phenine nanotube (pNT) is beautiful to see for its pleasing symmetry and simplicity, which is a stark contrast to its complex means of coming into being. Chemical synthesis of nanotubes is notoriously difficult and challenging, even more so if you wish to delicately control the structures in question to provide unique properties and functions.
Typical carbon nanotubes are famous for their perfect graphite structures without defects, but they vary widely in length and diameter. Isobe and his team wanted a single type of nanotube, a novel form with controlled defects within its nanometer-sized cylindrical structure allowing for additional molecules to add properties and functions.
The researchers' novel process of synthesis starts with benzene, a hexagonal ring of six carbon atoms. They use reactions to combine six of these benzenes to make a larger hexagonal ring called a cyclo-meta-phenylene (CMP). Platinum atoms are then used which allow four CMPs to form an open-ended cube. When the platinum is removed, the cube springs into a thick circle and this is furnished with bridging molecules on both ends enabling the tube shape.
It sounds complicated, but amazingly, this complex process successfully bonds the benzenes in the right way over 90 percent of the time. The key also lies in the symmetry of the molecule, which simplifies the process to assemble as many as 40 benzenes. These benzenes, also called phenines, are used as panels to form the nanometer-sized cylinder. The result is a novel nanotube structure with intentional periodic defects. Theoretical investigations show these defects imbue the nanotube with semiconductor characters.
"A crystal of pNT is also interesting: The pNT molecules are aligned and packed in a lattice rich with pores and voids," Isobe explains. "These nanopores can encapsulate various substances which imbue the pNT crystal with properties useful in electronic applications. One molecule we successfully embedded into pNT was a large carbon molecule called fullerene (C70)."
"A team lead by Kroto/Curl/Smalley discovered fullerenes in 1985. It is said that Sir Harold Kroto fell in love with the beautiful molecule," continues Isobe. "We feel the same way about pNT. We were shocked to see the molecular structure from crystallographic analysis. A perfect cylindrical structure with fourfold symmetry emerges from our chemical synthesis."
"After a few decades since the discovery, this beautiful molecule, fullerene, has found various utilities and applications," adds Isobe. "We hope that the beauty of our molecule is also pointing to unique properties and useful functions waiting to be discovered."
####
About University of TokyoThe University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 2,000 international students. Find out more at https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter at @UTokyo_News_en.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Research Contact
Professor Hiroyuki Isobe Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 JAPAN Tel: +81-3-5841-4777 Email:
Press Contacts
Ms. Kristina Awatsu Office of Communication, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033 JAPAN Tel: +81-3-5841-8737 E-mail:
Mr. Rohan Mehra Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654 JAPAN Tel: +81-3-5841-0876 Email:
Copyright © University of Tokyo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
![]() Laboratory of Physical Organic Chemistry:
Laboratory of Physical Organic Chemistry:
![]() ERATO Isobe Degenerate π-Integration Project:
ERATO Isobe Degenerate π-Integration Project:
News and information
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Chemistry
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods
![]() Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() New protocol for assessing the safety of nanomaterials July 1st, 2022
New protocol for assessing the safety of nanomaterials July 1st, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
