

| Date | 31st, Jan 2019 |
|---|
Home > Press > Fluid-inspired material self-heals before your eyes: Coating for metals rapidly heals over scratches and scrapes to prevent corrosion
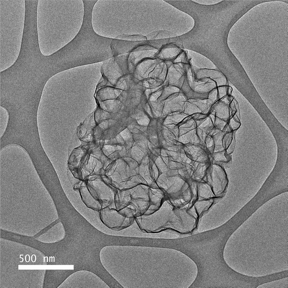 Oil in a graphene network
Kristin Samuelson
Oil in a graphene network
Kristin Samuelson
Abstract: Novel material works by trapping oil within pockets of graphene When scratched, network releases free oil to readily flow and heal within seconds Could address localized corrosion, which causes large, metal structures to fail Works underwater, in harsh chemical environments and when subjected to strong turbulence
Evanston, IL | Posted on January 30th, 2019
It's hard to believe that a tiny crack could take down a gigantic metal structure. But sometimes bridges collapse, pipelines rupture and fuselages detach from airplanes due to hard-to-detect corrosion in tiny cracks, scratches and dents.
A Northwestern University team has developed a new coating strategy for metal that self-heals within seconds when scratched, scraped or cracked. The novel material could prevent these tiny defects from turning into localized corrosion, which can cause major structures to fail.
'Localized corrosion is extremely dangerous,' said Jiaxing Huang, who led the research. 'It is hard to prevent, hard to predict and hard to detect, but it can lead to catastrophic failure.'
When damaged by scratches and cracks, Huang's patent-pending system readily flows and reconnects to rapidly heal right before the eyes. (Watch video.) The researchers demonstrated that the material can heal repeatedly ' even after scratching the exact same spot nearly 200 times in a row.
The study was published today (Jan. 28) in Research, the first Science Partner Journal recently launched by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in collaboration with the China Association for Science and Technology (CAST). Huang is a professor of materials science and engineering in Northwestern's McCormick School of Engineering.
While a few self-healing coatings already exist, those systems typically work for nanometer- to micron-sized damages. To develop a coating that can heal larger scratches in the millimeter-scale, Huang and his team looked to fluid.
'When a boat cuts through water, the water goes right back together,' Huang said. 'The 'cut' quickly heals because water flows readily. We were inspired to realize that fluids, such as oils, are the ultimate self-healing system.'
But common oils flows too readily, Huang noted. So he and his team needed to develop a system with contradicting properties: fluidic enough to flow automatically but not so fluidic that it drips off the metal's surface.
The team met the challenge by creating a network of lightweight particles ' in this case graphene capsules ' to thicken the oil. The network fixes the oil coating, keeping it from dripping. But when the network is damaged by a crack or scratch, it releases the oil to flow readily and reconnect. Huang said the material can be made with any hollow, lightweight particle ' not just graphene.
'The particles essentially immobilize the oil film,' Huang said. 'So it stays in place.'
The coating not only sticks, but it sticks well ' even underwater and in harsh chemical environments, such as acid baths. Huang imagines that it could be painted onto bridges and boats that are naturally submerged underwater as well as metal structures near leaked or spilled highly corrosive fluids. The coating can also withstand strong turbulence and stick to sharp corners without budging. When brushed onto a surface from underwater, the coating goes on evenly without trapping tiny bubbles of air or moisture that often lead to pin holes and corrosion.
'Self-healing microcapsule-thickened oil barrier coatings' was supported by the Office of Naval Research (ONR N000141612838). Graduate student Alane Lim and Chenlong Cui, a former member of Huang's research group, served as the paper's co-first authors.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Amanda Morris847-467-6790
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
![]() A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
![]() OCSiAl expands its graphene nanotube production capacities to Europe June 17th, 2022
OCSiAl expands its graphene nanotube production capacities to Europe June 17th, 2022
![]() Bumps could smooth quantum investigations: Rice University models show unique properties of 2D materials stressed by contoured substrates June 10th, 2022
Bumps could smooth quantum investigations: Rice University models show unique properties of 2D materials stressed by contoured substrates June 10th, 2022
Self-repairing Materials
![]() Materials scientists learn how to make liquid crystal shape-shift September 25th, 2020
Materials scientists learn how to make liquid crystal shape-shift September 25th, 2020
![]() Self-driving microrobots December 10th, 2019
Self-driving microrobots December 10th, 2019
![]() Disruptive by Design: Nano Now February 1st, 2019
Disruptive by Design: Nano Now February 1st, 2019
![]() Manufacturing microspheres: Technique mass-produces uniform, encapsulated particles for pharmaceuticals, many other uses October 6th, 2016
Manufacturing microspheres: Technique mass-produces uniform, encapsulated particles for pharmaceuticals, many other uses October 6th, 2016
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
![]() UNC Charlotte-led team invents new anticoagulant platform, offering hope for advances for heart surgery, dialysis, other procedures July 15th, 2022
UNC Charlotte-led team invents new anticoagulant platform, offering hope for advances for heart surgery, dialysis, other procedures July 15th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() New protocol for assessing the safety of nanomaterials July 1st, 2022
New protocol for assessing the safety of nanomaterials July 1st, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Military
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
