

| Date | 22nd, Feb 2019 |
|---|
Home > Press > High-speed surveillance in solar cells catches recombination red-handed: Researchers at Osaka University introduce a new time-resolved microscopy method that allows them to monitor the trajectories of fast-moving charged particles at unprecedented rates
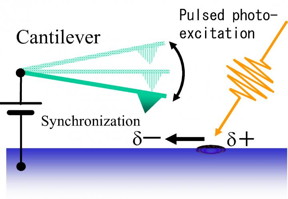 This is a schematic diagram illustrating the principle of tip-synchronized time-resolved electrostatic force microscopy.
CREDIT
Osaka University
This is a schematic diagram illustrating the principle of tip-synchronized time-resolved electrostatic force microscopy.
CREDIT
Osaka University
Abstract: A research team at Osaka University has developed an improved method for producing microscope images that can spot speedy electrons zipping through nanomaterials used in solar panels. By applying laser light to the device at just the right times, this group achieved nanosecond time resolution for the first time while maintaining the magnification. This work could improve the quality of photovoltaic materials for devices such as solar panels by helping to identify and eliminate inefficiencies during the manufacturing process.
Osaka, Japan | Posted on February 21st, 2019
Surveillance cameras are ubiquitous, and extremely valuable to the police when trying to catch thieves. However, cameras that record only a single movie frame per minute would be useless for apprehending speedy robbers who can make their getaway in less than sixty seconds. Solar panels harness the power of the sun when electrons become excited to a higher energy level, leaving a void, or "hole", behind. However, if an electron recombines with a hole before reaching the electrode, the harvested energy is lost, "robbing" the device of critical efficiency.
Currently available microscopy methods are too slow to catch the miscreants in the act. So the team at Osaka used electrostatic force microscopy (EFM), in which a tiny, vibrating cantilever tip is made sensitive to electric charges passing beneath it. EFM is still usually too slow to watch electrons and holes in motion, but their key innovation was to apply synchronized laser pulses that hit the sample at the same point of the cantilever's oscillation. By altering the delay time between the start of the cycle and the laser pulse, they were able to create a movie with frames as fast as 300 nanoseconds. "This is the first time anyone was able to combine nanosecond time resolution without sacrificing magnification," said lead author Kento Araki.
When the researchers probed the "scene of the crime", they were able to obtain video evidence of recombination as it was occurring. This method may be extremely useful for designing more efficient solar panels by reducing the energy losses due to recombination. According to senior author Takuya Matsumoto, "the research is also potentially useful for the study of catalysts or batteries that depend on light activation."
####
About Osaka UniversityOsaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan's most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university's ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum. Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/top
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Saori Obayashi
81-661-055-886
Copyright © Osaka University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
Imaging
News and information
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Tools
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore�s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore�s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
![]() New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
![]() Snapshot measurement of single nanostructure�s circular dichroism March 25th, 2022
Snapshot measurement of single nanostructure�s circular dichroism March 25th, 2022
Energy
![]() Generating power where seawater and river water meet July 22nd, 2022
Generating power where seawater and river water meet July 22nd, 2022
![]() A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes July 8th, 2022
Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes July 8th, 2022
![]() Key in increasing efficiency of next-generation solar cell, found in �light absorption capacity�! July 1st, 2022
Key in increasing efficiency of next-generation solar cell, found in �light absorption capacity�! July 1st, 2022
