

| Date | 9th, Mar 2019 |
|---|
Home > Press > The moir� patterns of three layers change the electronic properties of graphene
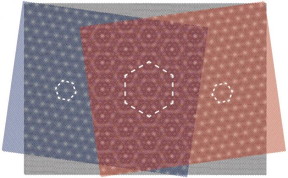 A graphene layer (black) of hexagonally arranged carbon atoms is placed between two layers of boron nitride atoms, which are also arranged hexagonally with a slightly different size. The overlap creates honeycomb patterns in various sizes.
CREDIT
Swiss Nanoscience Institute, University of Basel
A graphene layer (black) of hexagonally arranged carbon atoms is placed between two layers of boron nitride atoms, which are also arranged hexagonally with a slightly different size. The overlap creates honeycomb patterns in various sizes.
CREDIT
Swiss Nanoscience Institute, University of Basel
Abstract: Combining an atomically thin graphene and a boron nitride layer at a slightly rotated angle changes their electrical properties. Physicists at the University of Basel have now shown for the first time the combination with a third layer can result in new material properties also in a three-layer sandwich of carbon and boron nitride. This significantly increases the number of potential synthetic materials, report the researchers in the scientific journal Nano Letters.
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on March 8th, 2019
Last year, researchers in the US caused a big stir when they showed that rotating two stacked graphene layers by a "magical" angle of 1.1 degrees turns graphene superconducting - a striking example of how the combination of atomically thin materials can produce completely new electrical properties.
Precision alignment
Scientists from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel have now taken this concept one step further. They placed a layer of graphene between two boron nitride layers, which is often serves to protect the sensitive carbon structure. Doing so, they aligned the layers very precisely with the crystal lattice of the graphene.
The effect observed by the physicists in Professor Christian Sch�nenberger's team is commonly known as a moir� pattern: when two regular patterns are superimposed, a new pattern results with a larger periodic lattice.
New three-layer superlattice
Lujun Wang, a member of the SNI PhD School and researcher in Sch�nenberger's team, also observed effects of this kind of superlattice when he combined layers of boron nitride and graphene. The atoms are arranged hexagonally in all layers. If they are stacked on top of each other, larger regular patterns emerge, with a size depending on the angle between the layers.
It had already been shown that this works with a two-layer combination of graphene and boron nitride, but the effects due to a second boron nitride layer had not yet been found.
When the physicists from Basel experimented with three layers, two superlattices were formed between the graphene and the upper and the lower boron nitride layer, respectively. The superposition of all three layers created an even larger superstructure than possible with only one layer.
Scientists are very interested in these types of synthetic materials, since the different moir� patterns can be used to change or artificially produce new electronic material properties.
"To put it simply, the atomic patterns determine the behavior of electrons in a material, and we are combining different naturally occurring patterns to create new synthetic materials," explains Dr. Andreas Baumgartner, who supervised the project. "Now we have discovered effects in these tailor-made electronic devices that are consistent with a three-layer superstructure," he adds.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Ylenia Sartorel
@UniBasel_en
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Superconductivity
![]() U-M researchers untangle the physics of high-temperature superconductors August 19th, 2022
U-M researchers untangle the physics of high-temperature superconductors August 19th, 2022
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
![]() Controlled synthesis of crystal flakes paves path for advanced future electronics June 17th, 2022
Controlled synthesis of crystal flakes paves path for advanced future electronics June 17th, 2022
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene July 22nd, 2022
![]() A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
A novel graphene based NiSe2 nanocrystalline array for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction July 15th, 2022
Videos/Movies
![]() Scientists prepare for the world�s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world�s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
![]() Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
![]() OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
![]() Nanotube fibers stand strong -- but for how long? Rice scientists calculate how carbon nanotubes and their fibers experience fatigue December 24th, 2021
Nanotube fibers stand strong -- but for how long? Rice scientists calculate how carbon nanotubes and their fibers experience fatigue December 24th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Rice team eyes cells for sophisticated data storage: National Science Foundation backs effort to turn living cells into equivalent of computer RAM August 19th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
Scientists unravel �Hall effect� mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices August 19th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
