

| Date | 30th, Mar 2019 |
|---|
Home > Press > Fullerenes bridge conductive gap in organic photovoltaics: Efficient cathode interlayers made of ionene polymers refined with pendant fullerenes
 � Wiley-VCH
� Wiley-VCH
Abstract: Organic photovoltaics have achieved remarkably high efficiencies, but finding optimum combinations of materials for high-performance organic solar cells, which are also economically competitive, still presents a challenge. Researchers from the United States and China have now developed an innovative interlayer material to improve device stability and electrode performance. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, the authors describe their fullerene-spiked, readily processable ionene polymer, which boosts the power conversion efficiency of organic solar cells.
Hoboken, NJ | Posted on March 29th, 2019
In contrast to common silicon-based solar cells, organic photovoltaics (OPVs) involve organic molecules in solar power generation. Materials in OPVs are abundant and processable, cheap and lightweight, and the modules can be made flexible and with tunable properties. The major disadvantage of such materials is that achieving longevity and high performance requires elaborate settings and architectures. Optimized combinations of materials that match the electrodes remain elusive.
Silver or gold metals form air-stable, processable cathodes, but they also lower the device potential. To overcome this problem, Yao Lui at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (China), and Thomas Russell and Todd Emrick at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst (USA), and their research groups, have developed a novel polymeric material to serve as an interlayer between the electrode and the active layer. This interlayer must be conductive and must lower the work function of the cathode by providing an interfacial dipole.
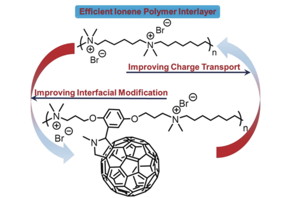
As an interlayer material, the researchers investigated a novel class of charged polymers, the ionene polymers. "Ionene polymers are polycations in which the charged moieties are positioned within the polymer backbone rather than as pendant groups," the authors explain. This leads to a higher charge distribution than in conventional cationic polymers, and in addition, better tunability. Ionene polymers provide a useful interfacial dipole, but alone, they lack the required conductivity.
Therefore, the authors included fullerenes in the structural framework of the polymer layer. So-called "bucky balls"--fullerene spheres made solely from carbon--are already used as common acceptor molecules in OPV devices. They are highly conductive and have many other favorable properties.
The scientists prepared the fullerene-ionene interlayer material by innovating on conventional step-growth polymerization chemistry with novel, functional monomers. They assembled the OPV devices and included an interlayer. The result was an impressive boost in power conversion efficiency--on average three-fold--when compared to devices without the interlayer. Efficiencies of over 10% point to further applicability of these modular devices.
This work shows that a relatively simple modification to the composition of materials can improve the efficiency in organic electronics and can overcome intrinsic problems related to the combination of hard (electrodes) and soft (active-layered) materials.
###
About the Author
Thomas P. Russell is the Silvio O. Conte Distinguished Professor at the Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, MA (USA). His research is focused on the interesting properties of polymers, including the morphology of polymer-based photovoltaic materials. Todd Emrick is a Professor in the Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, MA (USA), and he investigates synthetic organic/polymer chemistry. Yao Liu is a Professor at Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Soft Matter Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing (China). His research is focused on organic electronics and functional materials in devices.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Mario Mueller
Copyright © Wiley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Two opposing approaches could give lithium-sulfur batteries a leg up over lithium-ion July 1st, 2022
Two opposing approaches could give lithium-sulfur batteries a leg up over lithium-ion July 1st, 2022
![]() Efficiently processing high-quality periodic nanostructures with ultrafast laser July 1st, 2022
Efficiently processing high-quality periodic nanostructures with ultrafast laser July 1st, 2022
![]() Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities July 1st, 2022
Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities July 1st, 2022
Organic Electronics
![]() Flexing the power of a conductive polymer: A new material holds promise for the next generation of organic electronics June 24th, 2022
Flexing the power of a conductive polymer: A new material holds promise for the next generation of organic electronics June 24th, 2022
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Sieving carbons: Ideal anodes for high-energy sodium-ion batteries July 1st, 2022
Sieving carbons: Ideal anodes for high-energy sodium-ion batteries July 1st, 2022
![]() An artificial intelligence probe help see tumor malignancy July 1st, 2022
An artificial intelligence probe help see tumor malignancy July 1st, 2022
![]() Photon-controlled diode: an optoelectronic device with a new signal processing behavior July 1st, 2022
Photon-controlled diode: an optoelectronic device with a new signal processing behavior July 1st, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() CEA and Startup C12 Join Forces to Develop Next-Generation Quantum Computers with Multi-Qubit Chips at Wafer Scale March 25th, 2022
CEA and Startup C12 Join Forces to Develop Next-Generation Quantum Computers with Multi-Qubit Chips at Wafer Scale March 25th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Sieving carbons: Ideal anodes for high-energy sodium-ion batteries July 1st, 2022
Sieving carbons: Ideal anodes for high-energy sodium-ion batteries July 1st, 2022
![]() Efficiently processing high-quality periodic nanostructures with ultrafast laser July 1st, 2022
Efficiently processing high-quality periodic nanostructures with ultrafast laser July 1st, 2022
![]() Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities July 1st, 2022
Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities July 1st, 2022
Announcements
![]() Two opposing approaches could give lithium-sulfur batteries a leg up over lithium-ion July 1st, 2022
Two opposing approaches could give lithium-sulfur batteries a leg up over lithium-ion July 1st, 2022
![]() Efficiently processing high-quality periodic nanostructures with ultrafast laser July 1st, 2022
Efficiently processing high-quality periodic nanostructures with ultrafast laser July 1st, 2022
![]() Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities July 1st, 2022
Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities July 1st, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Sieving carbons: Ideal anodes for high-energy sodium-ion batteries July 1st, 2022
Sieving carbons: Ideal anodes for high-energy sodium-ion batteries July 1st, 2022
![]() An artificial intelligence probe help see tumor malignancy July 1st, 2022
An artificial intelligence probe help see tumor malignancy July 1st, 2022
![]() Photon-controlled diode: an optoelectronic device with a new signal processing behavior July 1st, 2022
Photon-controlled diode: an optoelectronic device with a new signal processing behavior July 1st, 2022
Energy
![]() Key in increasing efficiency of next-generation solar cell, found in �light absorption capacity�! July 1st, 2022
Key in increasing efficiency of next-generation solar cell, found in �light absorption capacity�! July 1st, 2022
![]() Solving the solar energy storage problem with rechargeable batteries that can convert and store energy at once June 24th, 2022
Solving the solar energy storage problem with rechargeable batteries that can convert and store energy at once June 24th, 2022
![]() Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Key in increasing efficiency of next-generation solar cell, found in �light absorption capacity�! July 1st, 2022
Key in increasing efficiency of next-generation solar cell, found in �light absorption capacity�! July 1st, 2022
![]() Solving the solar energy storage problem with rechargeable batteries that can convert and store energy at once June 24th, 2022
Solving the solar energy storage problem with rechargeable batteries that can convert and store energy at once June 24th, 2022
![]() USTC found a pathway to high-quality ZnSe quantum wires April 8th, 2022
USTC found a pathway to high-quality ZnSe quantum wires April 8th, 2022
![]() Graphene crystals grow better under copper cover April 1st, 2022
Graphene crystals grow better under copper cover April 1st, 2022
