

| Date | 7th, Aug 2021 |
|---|
Home > Press > Quantum computing enables unprecedented materials science simulations: Multi-institutional team provides a foundation for unraveling the mysteries of magnetic materials
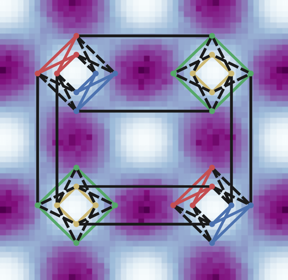 Researchers used a D-Wave quantum computer chip to create this simulation of a sample material with results comparable to those of real-world experiments.
CREDIT
Image courtesy of Paul Kairys
Researchers used a D-Wave quantum computer chip to create this simulation of a sample material with results comparable to those of real-world experiments.
CREDIT
Image courtesy of Paul Kairys
Abstract: The ScienceResearchers have for the first time used a quantum computer to generate accurate results from materials science simulations that can be verified with practical techniques. The team used a form of quantum computing called quantum annealing. This approach uses quantum physics to simplify a computer model. The team overcame quantum hardware limitations by programming various parameters into a materials science model. Next, they embedded the model into team member D-Wave�s 2000Q quantum computer.
Washington, DC | Posted on August 6th, 2021
The ImpactThe results from the simulation strongly resembled the output from real-world experiments. This demonstrates that quantum resources are capable of studying the magnetic structure and properties of magnetic materials. Eventually, such simulations on quantum computers could be more accurate and complex than simulations on classical digital computers. This would provide precise answers to materials science questions instead of approximations. It would also lead to a better understanding of spin liquids and spin ices. These are quantum states of matter that are potentially useful for data storage and other applications.
SummaryUsing the largest quantum computer available at the time, researchers completed the largest simulation possible for the Ising model, a mathematical model of ferromagnetism. The research provides a foundation to streamline future efforts on next-generation quantum computers. Although quantum resources have previously simulated small molecules to examine chemical or material systems, studying massive magnetic materials containing thousands of atoms would not have been possible on a smaller system. By using a Monte Carlo simulation technique powered by the quantum evolution of the Ising model, the team gained valuable insights into the formation of a phenomenon known as fractional magnetization plateaus within materials called rare earth tetraborides in microscopic detail. This exotic phenomenon occurs in frustrated materials when an applied magnetic field, which normally causes all spins in a material to point in one direction, affects only some spins in the usual way while others point in the opposite direction instead.
FundingThis work was funded by the Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science Early Career Research Program. Access to the D-Wave 2000Q system was provided through the Quantum Computing User Program managed by the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility, a DOE Office of Science user facility located at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). Research performed at ORNL�s Spallation Neutron Source, also a DOE Office of Science user facility located at ORNL, was supported by the DOE Office of Science. All the individuals and institutions involved with this research are members of the Quantum Science Center, a DOE Quantum Information Science Research Center established at ORNL in 2020.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Michael Church
Office: 505-358-1481
Copyright © U.S. Department of Energy
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
![]() Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
![]() Bumps could smooth quantum investigations: Rice University models show unique properties of 2D materials stressed by contoured substrates June 10th, 2022
Bumps could smooth quantum investigations: Rice University models show unique properties of 2D materials stressed by contoured substrates June 10th, 2022
![]() Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Electron-phonon coupling assisted universal red luminescence of o-phenylenediamine-based CDs June 10th, 2022
Electron-phonon coupling assisted universal red luminescence of o-phenylenediamine-based CDs June 10th, 2022
![]() Marching to the Cadence of Electronics: Innovation A new paper in Nature validates technology developed by John Bowers and collaborators June 10th, 2022
Marching to the Cadence of Electronics: Innovation A new paper in Nature validates technology developed by John Bowers and collaborators June 10th, 2022
![]() Small materials may be key to reducing cardiovascular disease deaths, researchers say June 10th, 2022
Small materials may be key to reducing cardiovascular disease deaths, researchers say June 10th, 2022
![]() Decoding a key part of the cell, atom by atom June 10th, 2022
Decoding a key part of the cell, atom by atom June 10th, 2022
Quantum Computing
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
![]() Bumps could smooth quantum investigations: Rice University models show unique properties of 2D materials stressed by contoured substrates June 10th, 2022
Bumps could smooth quantum investigations: Rice University models show unique properties of 2D materials stressed by contoured substrates June 10th, 2022
![]() A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() New route to build materials out of tiny particles May 27th, 2022
New route to build materials out of tiny particles May 27th, 2022
![]() A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Decoding a key part of the cell, atom by atom June 10th, 2022
Decoding a key part of the cell, atom by atom June 10th, 2022
![]() Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
Organic water splitters get a boost June 10th, 2022
