

| Date | 3rd, Dec 2021 |
|---|
Home > Press > Development of a single-process platform for the manufacture of graphene quantum dots: Precisely controls the bonding configuration of heteroatoms in graphene quantum dots through simple chemical processes. Practical application and commercialization in various fields is expected
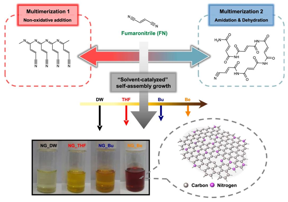 Schematic diagram of the possible formation mechanisms of NGs through the thermolytic self-assembly reaction of FN, and photographs of their ethanol solution preparation under four different solvent systems.
CREDIT
Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST)
Schematic diagram of the possible formation mechanisms of NGs through the thermolytic self-assembly reaction of FN, and photographs of their ethanol solution preparation under four different solvent systems.
CREDIT
Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST)
Abstract: Graphene consists of a planar structure, with carbon atoms connected in a hexagonal shape that resembles a beehive. When graphene is reduced to several nanometers (nm) in size, it becomes a graphene quantum dot that exhibits fluorescent and semiconductor properties. Graphene quantum dots can be used in various applications as a novel material, including display screens, solar cells, secondary batteries, bioimaging, lighting, photocatalysis, and sensors. Interest in graphene quantum dots is growing, because recent research has demonstrated that controlling the proportion of heteroatoms (such as nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorous) within the carbon structures of certain materials enhances their optical, electrical, and catalytic properties.
Sejong, Korea | Posted on December 3rd, 2021
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok-Jin Yoon) reported that the research team led by Dr. Byung-Joon Moon and Dr. Sukang Bae of the Functional Composite Materials Research Center have developed a technique to precisely control the bonding structure of single heteroatoms in the graphene quantum dot, which is a zero-dimensional carbon nanomaterial, through simple chemical reaction control; and that they identified the relevant reaction mechanisms.
With the aim of controlling heteroatom incorporation within the graphene quantum dot, researchers have previously investigated using additives that introduce the heteroatom into the dot after the dot itself has already been synthesized. The dot then had to be purified further, so this method added several steps to the overall fabrication process. Another method that was studied involved the simultaneous use of multiple organic precursors (which are the main ingredients for dot synthesis), along with the additives that contain the heteroatom. However, these methods had significant disadvantages, including reduced crystallinity in the final product and lower overall reaction yield, since several additional purification steps had to be implemented. Furthermore, in order to obtain quantum dots with the chemical compositions desired by manufacturers, various reaction conditions, such as the proportion of additives, would have to be optimized. This would inevitably lead to increases in the overall duration of the process and the manufacturing cost per unit.
The conventional fabrication method uses acidic precursors or solutions, and thus requires neutralization and purification steps. Conversely, the newly developed process uses weakly alkaline precursors that are neutralized during synthesis, meaning this process has the advantage that the produced graphene quantum dots require no additional processing before they are ready to use.
The research team also used computer modeling based on computational chemistry to discover that the solvent used in the synthesis process of graphene quantum dots affects the oxidation of the organic precursor, fumaronitrile, which also contains the heteroatoms (nitrogen). This implied that the solvent type ultimately determines the chemical composition of the final graphene quantum dot product. Furthermore, the theoretical oxidation energy value of the organic precursor, which was calculated based on the particular solvent used, was experimentally proven to have the ability to predict the approximate chemical composition of the final graphene quantum dot.
Dr. Sukang Bae of KIST stated, "We have developed a new platform technology that allows us to synthesize graphene quantum dots by selectively adjusting the chemical composition of heteroatoms with a single synthetic process, without the use of other additives other than organic precursors such as fumaronitrile," and added, "Because we discovered a way to achieve the mass synthesis of graphene quantum dots without additional post-processing or purification processes, we were able to reduce the overall processing time and increase the economic feasibility of the synthetic procedure."
Furthermore, this achievement is expected to drive the development of nanocarbon materials, as well as increase economic opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises, and further the growth of human resources in connection with the expansion of the carbon-materials industry, which is the regional strategic industry of the Jeollabuk-do Province.
####
About National Research Council of Science & Technology(NST)The Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST). Founded as the first multidisciplinary government-funded research institute in Korea, KIST established a national development strategy based on science and technology and disseminated various essential industrial technologies. Now, half a century later, KIST is elevating Korea's status in the field of science and technology through world-leading fundamental technology R&D. Looking to the future, KIST will continue to strive to be a premier research institute, pursuing a brighter future for Korea and all of humanity.
This study was conducted as a institutional research program and the Materials Part Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (Minister Seung-Wook Moon). The results of the study were published in the international journal, 'Nature Communications' (IF: 14.919, JCR(%): 4.795%)
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Young Mi KimNational Research Council of Science & Technology
Office: 82-442-877-376Expert Contacts
Dr. Sukang BaeKorea Institute of Science and Technology
Office: +82-2-958-8158Kim, Dohyun (PR Department)Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Office: +82-2-958-6344
Copyright © National Research Council of Science & Technology(NST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices empowered by graphene May 6th, 2022
Dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices empowered by graphene May 6th, 2022
![]() Graphene crystals grow better under copper cover April 1st, 2022
Graphene crystals grow better under copper cover April 1st, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() New substance classes for nanomaterials: Nano spheres and diamond slivers made of silicon and germanium: Potential applications as nano semiconductor materials September 10th, 2021
New substance classes for nanomaterials: Nano spheres and diamond slivers made of silicon and germanium: Potential applications as nano semiconductor materials September 10th, 2021
![]() �Missing jigsaw piece�: engineers make critical advance in quantum computer design August 20th, 2021
�Missing jigsaw piece�: engineers make critical advance in quantum computer design August 20th, 2021
