

| Date | 11th, Dec 2021 |
|---|
Home > Press > Development of a high-energy-resolution, LaB6 nanowire-based field emission gun: Electron source enables atomic resolution TEM observation
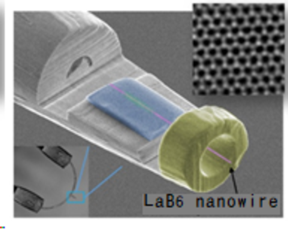 SEM image of the LaB6 nanowire-based electron source. An atomic resolution image of single-layer graphene taken by a TEM equipped with this electron source is shown in the boxed image at upper right.
CREDIT
Koji Kimoto National Institute for Materials Science Tel: +81-29-860-4402 Email: KIMOTO.Koji@nims.go.jp Zhang Han National Institute for Materials Science Email: Zhang.han@nims.go.jp
SEM image of the LaB6 nanowire-based electron source. An atomic resolution image of single-layer graphene taken by a TEM equipped with this electron source is shown in the boxed image at upper right.
CREDIT
Koji Kimoto National Institute for Materials Science Tel: +81-29-860-4402 Email: KIMOTO.Koji@nims.go.jp Zhang Han National Institute for Materials Science Email: Zhang.han@nims.go.jp
Abstract: The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) and JEOL, Ltd. have developed a lanthanum hexaboride (LaB6) nanowire-based field emission gun that is installable on an aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope (TEM). This combined unit is able to perform atomic resolution observation at an energy resolution of 0.2 eV�the highest resolution ever recorded for non-monochromatic electron guns�with a high current stability of 0.4%.
Sengen, Japan | Posted on December 10th, 2021
Unsuccessful efforts have been made for more than 20 years to develop field emission guns using theoretically high-performance nano materials. It has been found challenging to integrate a nanowire-based field emission gun into an electron microscope without undermining its physical properties, such as lives and stability. For this reason, commercially available field emission guns are still equipped with tungsten needles developed more than half a century ago.
This NIMS-JEOL research team 1) developed techniques to chemically synthesize and grow high-purity, single-crystal nanowires of LaB6, known to be an excellent electron-emitting hot cathode material, 2) designed an electron source mechanism capable of efficiently emitting electrons and 3) developed techniques to extract a single nanowire and integrate it into an optimized electron source structure.
The LaB6 nanowire-based electron source has a number of advantages: relatively moderate vacuum condition requirements, very high current stability, low extraction voltage, narrow electron beam energy distribution width and high brightness. This electron source may be applicable to the development of next-generation field emission electron microscopes with higher spatial and energy resolution�potentially valuable tools in the semiconductor and medical fields.
***
This project was carried out by a team of NIMS researchers (Han Zhang, Cretu Ovidiu, Koji Kimoto, Takeshi Kasaya, Hideki T. Miyazaki, Naohito Tsujii, Hongxin Wang, Yasushi Yamauchi and Daisuke Fujita) and JEOL researchers (Yu Jimbo, Akira Niwata, Akihiro Ikeda, Akira Yasuhara, Shin-ichi Kitamura and Hironobu Manabe).
This research was published in the online version of Nature Nanotechnology on November 9, 2021, Japan Time (DOI: 10.1038/s41565-021-00999-w).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Yasufumi NakamichiNational Institute for Materials Science, Japan
Office: 81-29-859-2105Expert Contacts
Zhang HanNational Institute for Materials Science
Koji KimotoNational Institute for Materials Science
Copyright © National Institute for Materials Science, Japan
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Imaging
![]() Snapshot measurement of single nanostructure�s circular dichroism March 25th, 2022
Snapshot measurement of single nanostructure�s circular dichroism March 25th, 2022
![]() Better understanding superconductors with Higgs spectroscopy Prof. Stefan Kaiser from TU Dresden awarded ERC Consolidator Grant March 18th, 2022
Better understanding superconductors with Higgs spectroscopy Prof. Stefan Kaiser from TU Dresden awarded ERC Consolidator Grant March 18th, 2022
![]() Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Tools
![]() Snapshot measurement of single nanostructure�s circular dichroism March 25th, 2022
Snapshot measurement of single nanostructure�s circular dichroism March 25th, 2022
![]() Eyebrow-raising: Researchers reveal why nanowires stick to each other February 11th, 2022
Eyebrow-raising: Researchers reveal why nanowires stick to each other February 11th, 2022
![]() JEOL Introduces New Scanning Electron Microscope with �Simple SEM� Automation and Live Elemental and 3D Analysis January 14th, 2022
JEOL Introduces New Scanning Electron Microscope with �Simple SEM� Automation and Live Elemental and 3D Analysis January 14th, 2022
![]() Super-resolved imaging of a single cold atom on a nanosecond timescale January 7th, 2022
Super-resolved imaging of a single cold atom on a nanosecond timescale January 7th, 2022
