

| Date | 12th, Feb 2022 |
|---|
Home > Press > Scientists use DNA to assemble complex nanomaterials: Researchers create DNA nano-chambers with bonds that can control the assembly of targeted nanoparticle structures
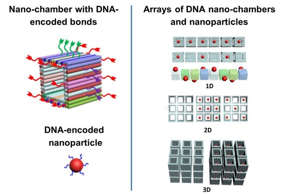 IMAGE: SEPARATELY ADDRESSABLE BONDS EXTENDING FROM EACH FACE OF THE CUBE-SHAPED DNA CHAMBER (LEFT) ARE ASSEMBLED INTO ARRAYS OF CHAMBERS CONTAINING NANOPARTICLES (RIGHT). view more
CREDIT: IMAGE COURTESY OF OLEG GANG, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY. PORTIONS APPEARED IN LIN, Z., ET AL., ENGINEERING ORGANIZATION OF DNA NANO-CHAMBERS THROUGH DIMENSIONALLY CONTROLLED AND MULTI-SEQUENCE ENCODED DIFFERENTIATED BONDS, J. AM. CHEM. SOC. 142, 17531 (2020).
IMAGE: SEPARATELY ADDRESSABLE BONDS EXTENDING FROM EACH FACE OF THE CUBE-SHAPED DNA CHAMBER (LEFT) ARE ASSEMBLED INTO ARRAYS OF CHAMBERS CONTAINING NANOPARTICLES (RIGHT). view more
CREDIT: IMAGE COURTESY OF OLEG GANG, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY. PORTIONS APPEARED IN LIN, Z., ET AL., ENGINEERING ORGANIZATION OF DNA NANO-CHAMBERS THROUGH DIMENSIONALLY CONTROLLED AND MULTI-SEQUENCE ENCODED DIFFERENTIATED BONDS, J. AM. CHEM. SOC. 142, 17531 (2020).
Abstract: The ScienceIn nature, DNA contains the instructions for the cells that allow life to grow, thrive, and reproduce. Researchers see great potential in DNA for its ability to direct assemble of a wide range of customized artificial materials. Scientists have developed a way to design and assemble artificial DNA objects tens of thousands of times smaller than a human hair. These objects can host nanoparticles and link them together into complex structures. Researchers recently extended this approach to include the tunable construction of complex 1, 2, and 3-dimensional structures. The method forms DNA strands into hollow cubes that can carry nanoparticle cargoes. The DNA strands that extend from the cube are encoded with specific assembly directions. This binding information allowed the scientists to precisely control the orientation of the objects in each direction at each step along the assembly pathway.
Washington, DC | Posted on February 11th, 2022
The ImpactScientists are excited about DNA-directed assembly for its potential in next-generation applications. For example, these materials could make nano-robots for use in manufacturing and medicine or new materials to harvest light for energy. This research controlled the creation of complex nanostructures using molecular design and nanoscale programming of DNA for assembly. This approach allows scientists to control the orientation and position of building blocks via each individual bond connecting those blocks. It represents an important advance in the use of DNA for assembling new materials.
SummaryThe assembly of nanoscale objects into complex, predetermined structures requires control over the type and direction of the linkages connecting those objects. Scientists have made progress in their ability to design complex nanoscale objects. However, researchers face challenges in precisely assembling these objects as designed with full control over how they bind together. This requires a fundamental understanding of the assembly pathways. In this research, scientists developed a straightforward strategy for creating a cube-shaped DNA nano chamber (DNC) with fully prearranged DNA bonds encoded with all the information needed to direct assembly as designed along each of the three axes of the chamber. The researchers built one-, two-, and three-dimensional ordered arrays of DNCs by fine tuning the directionality of DNA bonds. The researchers also developed computational methods to predict structure formation in these systems. The DNC can host nanoscale cargoes such as metal ions. This allows for the construction of complex organizations of nano cargoes with controlled architectures in a fully prescribed manner across much larger length scales. This effort was greatly enhanced by use of the Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) facilities at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN), a Department of Energy user facility. The researchers used the TEM to directly visualize the DNCs and their organized arrays. They used the X-ray scattering capabilities at the CFN and the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS II), another DOE user facility, to provide additional structural analysis.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Michael ChurchDOE/US Department of Energy
Office: 2028416299
Oleg GangColumbia University
Copyright © DOE/US Department of Energy
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
![]() Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
Laboratories
![]() A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
![]() Bacteria-killing drills get an upgrade Visible light triggers: Rice�s molecular machines to treat infections June 1st, 2022
Bacteria-killing drills get an upgrade Visible light triggers: Rice�s molecular machines to treat infections June 1st, 2022
![]() A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
A one-stop shop for quantum sensing materials May 27th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
![]() Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
Nanostructured fibers can impersonate human muscles June 3rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
Nanoscale bowtie antenna under optical and electrical excitations June 3rd, 2022
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() �Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
�Fruitcake� structure observed in organic polymers June 3rd, 2022
![]() Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
Progressive Medicinal and Herbal Nanoscience for Targeted Drug Delivery Systems June 3rd, 2022
![]() Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Artificial Intelligence Centered Cancer Nanomedicine: Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Bioethics June 3rd, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]() Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
Emerging vaccine nanotechnology June 3rd, 2022
![]() Bacteria-killing drills get an upgrade Visible light triggers: Rice�s molecular machines to treat infections June 1st, 2022
Bacteria-killing drills get an upgrade Visible light triggers: Rice�s molecular machines to treat infections June 1st, 2022
![]() Diabetes drug improves antibacterial treatment speed and effectiveness, researchers report May 27th, 2022
Diabetes drug improves antibacterial treatment speed and effectiveness, researchers report May 27th, 2022
![]() Oregon State University research pushes closer to new therapy for pancreatic cancer May 6th, 2022
Oregon State University research pushes closer to new therapy for pancreatic cancer May 6th, 2022
