

| Date | 4th, Apr 2022 |
|---|
 Credit: Tel Aviv University
Credit: Tel Aviv University
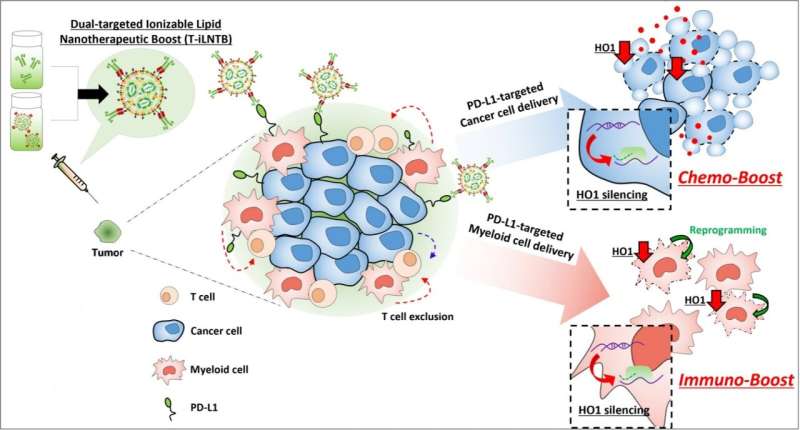
Researchers from Tel Aviv University proved that a drug delivery system based on lipid nanoparticles can utilize RNA to overcome resistance to both chemotherapy and immunotherapy in cancer treatments. The study opens a new path to a personalized and precisely targeted battle against cancer. The results were published in the scientific journal Advanced Materials.
The study was led by TAU Vice President for R&D Prof. Dan Peer, Head of the Laboratory of Precision Nanomedicine at the Shmunis School of Biomedicine and Cancer Research, Wise Faculty of Life Sciences, and a member of the Roman Abramovich Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, together with post-doctoral researcher Dr. Seok-Beom Yong of South Korea. The study was funded via an ERC grant from the European Union and a research scholarship from the Korean government.
Chemo-immunotherapy, which combines chemotherapy with immunotherapy, is considered the most advanced standard of care for various types of cancer. While chemotherapy destroys cancer cells, immunotherapy encourages the cells of the immune system to identify and attack the remaining cancer cells. However, many patients fail to respond to chemo-immunotherapy, which means that the treatment is not sufficiently targeted. Prof. Peer and his team are the first in the world to prove the feasibility of a drug delivery system based on lipid nanoparticles that release their load only at the specifically targeted cells—cancer cells for chemotherapy and immune cells for immunotherapy.
