

| Date | 7th, May 2022 |
|---|
Home > Press > Dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices empowered by graphene
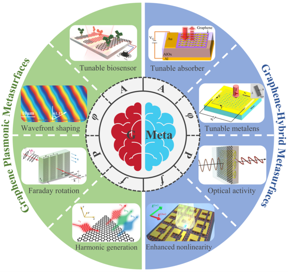 Overview of state-of-the-art selected functionalities of dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices empowered by graphene
CREDIT
OEA
Overview of state-of-the-art selected functionalities of dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices empowered by graphene
CREDIT
OEA
Abstract: A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2022.200098 overview dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices empowered by graphene.
Sichuan, China | Posted on May 6th, 2022
Metasurfaces, artificial subwavelength structured interfaces, exhibit unprecedented capabilities to manipulate electromagnetic (EM) waves ranging from visible to terahertz and microwave frequencies.
In the past decade, static metasurfaces and metadevices have been researched extensively. Due to the passive nature of building blocks in general made of metals and/or dielectrics, however, their functionalities cannot be actively tuned in situ after fabrication, which seriously impedes their application scenarios such as varifocal lens, dynamic holography, and beam steering in LiDAR. Motivated by those significant requirements, scientists have struggled for years to improve the dynamical tunability of metasurfaces, and introducing active materials or components into the passive metasurfaces has been proposed as the first thought strategy.
To date, various active materials and components such as transparent conducting oxides, phase-change materials, 2D materials (particularly graphene), varactor diodes, elastic materials, and micro-electro-mechanical systems, have been demonstrated theoretically and experimentally to empower the active tunability to metasurfaces and metadevices by applying external thermal, electrical, optical, and mechanical stimulus, giving rise to a new direction, i.e., dynamic (e.g. tunable, reconfigurable, programable, intelligent, and digital coding) metasurfaces and metadevices. It should be noted that although previous researches provide a major source of inspiration for dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices, each type of active materials and components holds a set of unique characteristics, provides encouraging opportunities, and also suffers from different limitations as well as challenges. Several excellent review articles published in recent years have focused on this area to discuss the aforementioned issues. However, a comprehensive review on graphene-based dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices is still absent, which are of equal and even more significance due to the extraordinary properties of graphene.
In this article the authors divide graphene-empowered dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices are divided into two categories, i.e., metasurfaces with building blocks of structured graphene and hybrid metasurfaces integrated with graphene, as shown in Fig. 1. The state-of-the-art developments in dynamic spectrum manipulation, wavefront shaping, polarization control, and frequency conversion are highly elaborated in near/far fields and global/local ways, respectively. Remaining challenges and potential future developments are also outlined and analyzed.
The authors believe that due to the intrinsic advantages of compact footprint, remarkable electrical tunability, broadband and high-speed operation, graphene and graphene-like 2D materials are propelling the EM wave manipulations using metasurfaces to a new height: from static to dynamic, which will certainly revolutionize EM wave manipulations and allow for future commercial applications.
Article reference: Zeng C, Lu H, Mao D, Du YQ, Hua H et al. Graphene-empowered dynamic metasurfaces and metadevices. Opto-Electron Adv 5, 200098 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.200098
Keywords metasurface / dynamic metasurface / graphene / graphene plasmons / light field manipulation / electromagnetic wave manipulation
# # # # # #
Chao Zeng is the associate professor of Northwestern Polytechnical University, mainly engaged in the research of micro/nanophotonics, nonlinear optics, and optical metasurfaces, and committed to providing new theories and technologies for novel light field manipulations, special fiber laser, and metadevices. To date, he has published 17 papers as first or corresponding author, which have been cited more than 400 times. One work is selected as the China�s Optics Important Achievements (2014). He has been awarded the Special Prize of President Scholarship for Postgraduate Students.
####
About Compuscript LtdOpto-Electronic Advances (OEA) is a high-impact, open access, peer reviewed monthly SCI journal with an impact factor of 9.682 (Journals Citation Reports for IF 2020). Since its launch in March 2018, OEA has been indexed in SCI, EI, DOAJ, Scopus, CA and ICI databases over the time and expanded its Editorial Board to 36 members from 17 countries and regions (average h-index 49).
The journal is published by The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, aiming at providing a platform for researchers, academicians, professionals, practitioners, and students to impart and share knowledge in the form of high quality empirical and theoretical research papers covering the topics of optics, photonics and optoelectronics.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Conor LovettCompuscript Ltd
Office: 353-614-75205
Copyright © Compuscript Ltd
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
![]() New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
![]() Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Graphene crystals grow better under copper cover April 1st, 2022
Graphene crystals grow better under copper cover April 1st, 2022
![]() Graphene gets enhanced by flashing: Rice process customizes one-, two- or three-element doping for applications March 31st, 2022
Graphene gets enhanced by flashing: Rice process customizes one-, two- or three-element doping for applications March 31st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() First integrated laser on lithium niobate chip: Research paves the way for high-powered telecommunication systems April 8th, 2022
First integrated laser on lithium niobate chip: Research paves the way for high-powered telecommunication systems April 8th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
![]() New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
![]() Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
![]() Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
![]() New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
New nanomechanical oscillators with record-low loss May 13th, 2022
![]() Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Small microring array enables large complex-valued matrix multiplication May 13th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022
Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022
![]() On-Chip Photodetection: Two-dimensional material heterojunctions hetero-integration May 13th, 2022
On-Chip Photodetection: Two-dimensional material heterojunctions hetero-integration May 13th, 2022
![]() Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
Engineering piezoelectricity and strain sensitivity in CdS to promote piezocatalytic hydrogen evolution May 13th, 2022
