

| Date | 10th, Jun 2022 |
|---|
Home > Press > Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis publishes method for the fast detection of a key antiviral: Researchers from China demonstrate a novel nanobody-based detection of recombinant human interferon ?2b using a strip test
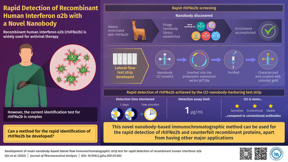 Development of novel-nanobody-based lateral-flow Immunochromatographic strip test for rapid detection of recombinant human interferon ?2b.
CREDIT
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
Development of novel-nanobody-based lateral-flow Immunochromatographic strip test for rapid detection of recombinant human interferon ?2b.
CREDIT
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
Abstract: Interferons are proteins that constitute an important part of our natural defense systems. These proteins also exhibit a remarkable antiviral activity. The recombinant human interferon ?2b (rhIFN?2b) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1986. It has been used ever since as an antiviral agent for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Despite its widespread applications, however, there remains an issue: the detection of rhIFN?2b is tedious and time-consuming.
Beilin, China | Posted on June 10th, 2022
Against this backdrop, researchers from China, in a new study, recently developed a novel method for the fast and efficient detection of rhIFN?2b. This paper was made available online on 8 July 2021 and was published in Volume 12 Issue 2 of the Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis in 30 April 2022.
To achieve this, they immobilized a novel ?nanobody? on a paper strip. The nanobody used in this method was originally derived from an Alpaca?a species of the South American camelid mammal. Subsequently, it was generated in the research laboratory using recombinant DNA technology?a technique used to ?subclone? DNA fragments in order to obtain high quantities of synthetic proteins. This is usually achieved using bacteria or other prokaryotic cells. A ?nanobody? is a functional fragment of a larger antibody. As the immobilized novel nanobody binds rhIFN?2b tightly and with high specificity, it was used for a rapid and fool-proof detection of rhIFN?2b.
According to Dr. Junzhi Wang, ?Owing to the advantages of nanobodies in reagent preservation, production, and cost, the lateral flow immunochromatography assay using nanobodies has a high potential to replace traditional antibody-based ligand-binding assays for a rapid identification test of recombinant protein therapeutics.?
The research team characterized the binding for the I22-rhIFN?2b interaction, i.e. binding between nanobody 122 and rhIFN?2b, using an Octet platform. The obtained data clearly indicated a tight binding. The binding specificity was further validated using Western blotting, a technique used to detect proteins using protein-specific antibodies.
?The rhIFN?2b products currently available in China include injections, injection powders, gels, and pastes. The immunochromatography strips can only be used to evaluate liquids or products in powder form that can be dissolved and applied to the strips. This is because the product needs to diffuse along the strip via capillary action; gels and pastes do not satisfy this requirement,? explains Dr. Wang.
Quite interestingly, the developed rhIFNa2b detection assay has a detection limit of 1 ?g/mL, which is lower than the existing limits. This makes it a more sensitive lab-based technique for rapid identification of rhIFN?2b. Another big advantage is the use of nanobodies for protein detection. This is because nanobodies can be obtained in an economical manner by harvesting inexpensive bacterial cells. Moreover, large volumes of nanobodies can be obtained with relative ease using routinely used laboratory techniques.
Dr. Wang summarizes, ?The operation time of rhIFN?2b identification was shortened from two days to a few minutes with our test. It can, therefore, meet the needs for rapid detection of this family of recombinant protein products on the market and provide a good foundation for improving the efficiency of market counterfeit detection. In the future, rapid detection could be carried out in an all-round manner.?
In summary, the newly developed method could pave the way for smoother, faster, and accurate detection of recombinant or artificially generated proteins, making for early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Fen QiuJournal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
Office: +86-131-5206-8068
Copyright © Cactus Communications
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
![]() New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
![]() Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
![]() New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
![]() Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
![]() From outside to inside: A rapid and precise total assessment method for cells: Researchers at Nara Institute of Science and Technology show that using four frequencies of applied voltage can improve the measurement of cell size and shape during impedance cytometry, enabling to en June 24th, 2022
From outside to inside: A rapid and precise total assessment method for cells: Researchers at Nara Institute of Science and Technology show that using four frequencies of applied voltage can improve the measurement of cell size and shape during impedance cytometry, enabling to en June 24th, 2022
![]() Disinfectant mechanism of nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles on SARS-CoV-2: Nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2 envelope, protein, and RNA, thereby impairing the virus?s ability to bind to host cells June 17th, 2022
Disinfectant mechanism of nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles on SARS-CoV-2: Nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2 envelope, protein, and RNA, thereby impairing the virus?s ability to bind to host cells June 17th, 2022
![]() New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
![]() Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
![]() New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
New technology helps reveal inner workings of human genome June 24th, 2022
![]() Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
![]() Quantum network nodes with warm atoms June 24th, 2022
Quantum network nodes with warm atoms June 24th, 2022
![]() Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios?are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics? June 24th, 2022
![]() From outside to inside: A rapid and precise total assessment method for cells: Researchers at Nara Institute of Science and Technology show that using four frequencies of applied voltage can improve the measurement of cell size and shape during impedance cytometry, enabling to en June 24th, 2022
From outside to inside: A rapid and precise total assessment method for cells: Researchers at Nara Institute of Science and Technology show that using four frequencies of applied voltage can improve the measurement of cell size and shape during impedance cytometry, enabling to en June 24th, 2022
![]() Disinfectant mechanism of nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles on SARS-CoV-2: Nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2 envelope, protein, and RNA, thereby impairing the virus?s ability to bind to host cells June 17th, 2022
Disinfectant mechanism of nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles on SARS-CoV-2: Nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2 envelope, protein, and RNA, thereby impairing the virus?s ability to bind to host cells June 17th, 2022
