A new method developed for finding optimal quantum operation sequences for quantum computers. Based on GRAPE, the new method systematically finds quantum operation sequences and enables efficient task execution. Expected to contribute to improving the performance of quantum computers and reducing environmental impact

The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT, President: TOKUDA Hideyuki, Ph.D.), Keio University (President: ITOH Kohei, Ph.D.), Tokyo University of Science (President: Dr. ISHIKAWA Masatoshi), The University of Tokyo (President: Dr. FUJII Teruo), succeeded for the first time in developing a method for systematically finding the optimal quantum operation sequence for a quantum computer*1.
For a quantum computer to perform a task, we need to write a sequence of quantum operations. Computer operators have written their own quantum operation sequences based on existing methods (recipes). We have developed a systematic method that applies optimal control theory (GRAPE*2 algorithm) to identify the theoretically optimal sequence from among all conceivable quantum operation sequences.
This method is expected to become a useful tool for medium-scale quantum computers and contribute to improving the performance of quantum computers and reducing environmental impact shortly.
This result was published in the American scientific journal “Physical Review A.”
Background
Quantum computers, which are currently under development, are expected to have a major impact on society. Their benefits include reducing the environmental burden by reducing energy consumption, finding new chemical substances for medical use, accelerating the search for materials for a cleaner environment, etc.
One of the big problems for quantum computers is that the quantum state is very sensitive to noise, so it is difficult to maintain it stably for a long time (maintaining a coherent quantum state). In order to obtain the best performance, it is necessary to complete the operations within the time that the coherent quantum state is maintained. There was a need for a method to identify the optimal sequences systematically.

Figure 1 Quantum operation sequence (conceptual diagram)The six horizontal blue lines represent six qubits, with the input on the left and the output on the right. Operations are executed from left to right. Each red square represents a 1-qubit operation, and each green vertical line connecting two blue lines represents a 2-qubit operation. The optimal quantum operation sequence is realized with the fewest operations.
Results
The research team has developed a systematic method to identify the optimal quantum operation sequence.
When a computer stores and processes information, all information is converted to a string of bits with values of 0 or 1. A quantum operation sequence is a computer program written in a human-readable language that is converted so that it can be processed by a quantum computer (see Figure 1). The quantum operation sequence consists of 1-qubit operations and 2-qubit operations. The best sequence is the one with the fewest operations and shows the best performance (the number of red squares and green vertical lines is the smallest).
The new method analyzes all possible sequences of elementary quantum operations using a computational algorithm called GRAPE, a numerical optimal control theory algorithm. Specifically, we create a table of quantum operation sequences and the performance index (fidelity F) for each sequence, ranging from thousands to millions, depending on the number of qubits and the number of operations under investigation. The optimal quantum operation sequence is systematically identified based on the accumulated data. Figure 2 shows the relationship between the length of the quantum operation sequence and its performance index, and it can be seen that if the number of qubits n is 4, five or more 2-qubit gates*3 are required.
It is also possible for the new method to analyze the complete list of all quantum operation sequences and evaluate conventional recipes. As such, it can provide a valuable tool for establishing benchmarks for past and future research on the performance of few-qubit quantum algorithms.
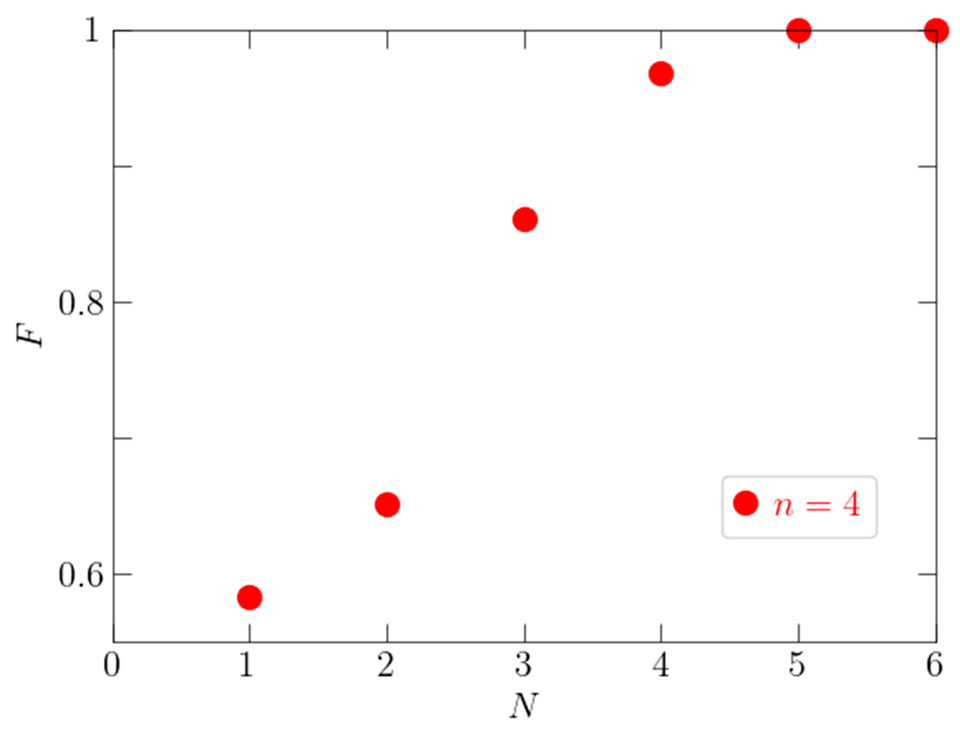 Figure 2 The maximum fidelity F that can be achieved when preparing four-qubit statesN is the number of 2-qubit gates used for state preparation (the green vertical line in Figure 1), F is the fidelity (if less than 1, the target state preparation is incomplete), and n is the number of qubits.
Figure 2 The maximum fidelity F that can be achieved when preparing four-qubit statesN is the number of 2-qubit gates used for state preparation (the green vertical line in Figure 1), F is the fidelity (if less than 1, the target state preparation is incomplete), and n is the number of qubits.
Future prospects
The systematic method to find the optimal quantum operation sequence for quantum computers is expected to become a useful tool for medium-scale quantum computers. Shortly, it is expected to improve the performance of quantum computers (see Figure 3) and contribute to reducing the burden on the environment.
We also found that many optimal sequences of quantum operations are excellent (see Appendix for details). This means that a probabilistic approach*5 could extend the applicability of this new method to larger tasks. Approaches based on analyzing large datasets suggest the possibility of integrating machine learning with our new method to enhance the predictive power further. In the future, the research team will apply the results obtained this time to the optimization of tasks obtained from actual quantum algorithms.
Source: Tokyo University of Science
You can offer your link to a page which is relevant to the topic of this post.


