

| Date | 23rd, Sep 2022 |
|---|
Home > Press > Heat-resistant nanophotonic material could help turn heat into electricity: The key to beating the heat is degrading the materials in advance
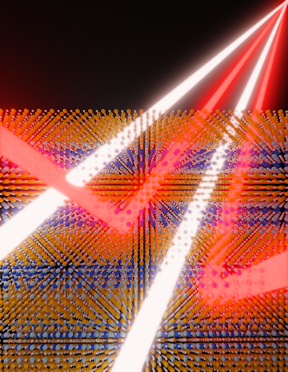 This artist�s rendering shows the material reflecting infra-red light while letting other wavelengths pass through. Image: Andrej Lenert, University of Michigan
This artist�s rendering shows the material reflecting infra-red light while letting other wavelengths pass through. Image: Andrej Lenert, University of Michigan
Abstract: A new nanophotonic material has broken records for high-temperature stability, potentially ushering in more efficient electricity production and opening a variety of new possibilities in the control and conversion of thermal radiation.
Ann Arbor, MI | Posted on September 23rd, 2022
Developed by a University of Michigan-led team of chemical and materials science engineers, the material controls the flow of infrared radiation and is stable at temperatures of 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit in air, a nearly twofold improvement over existing approaches.
The material uses a phenomenon called destructive interference to reflect infrared energy while letting shorter wavelengths pass through. This could potentially reduce heat waste in thermophotovoltaic cells, which convert heat into electricity but can't use infrared energy, by reflecting infrared waves back into the system. The material could also be useful in optical photovoltaics, thermal imaging, environmental barrier coatings, sensing, camouflage from infrared surveillance devices and other applications.
"It's similar to the way butterfly wings use wave interference to get their color. Butterfly wings are made up of colorless materials, but those materials are structured and patterned in a way that absorbs some wavelengths of white light but reflects others, producing the appearance of color," said Andrej Lenert, U-M assistant professor of chemical engineering and co-corresponding author of the study in Nature Photonics.
"This material does something similar with infrared energy. The challenging part has been preventing breakdown of that color-producing structure under high heat."
The approach is a major departure from the current state of engineered thermal emitters, which typically use foams and ceramics to limit infrared emissions. These materials are stable at high temperature but offer very limited control over which wavelengths they let through. Nanophotonics could offer much more tunable control, but past efforts haven't been stable at high temperatures, often melting or oxidizing (the process that forms rust on iron). In addition, many nanophotonic materials only maintain their stability in a vacuum.
The new material works toward solving that problem, besting the previous record for heat resistance among air-stable photonic crystals by more than 900 degrees Fahrenheit in open air. In addition, the material is tunable, enabling researchers to tweak it to modify energy for a wide variety of potential applications. The research team predicted that applying this material to existing TPVs will increase efficiency by 10% and believes that much greater efficiency gains will be possible with further optimization.
The team developed the solution by combining chemical engineering and materials science expertise. Lenert's chemical engineering team began by looking for materials that wouldn't mix even if they started to melt.
"The goal is to find materials that will maintain nice, crisp layers that reflect light in the way we want, even when things get very hot," Lenert said. "So we looked for materials with very different crystal structures, because they tend not to want to mix."
They hypothesized that a combination of rock salt and perovskite, a mineral made of calcium and titanium oxides, fit the bill. Collaborators at U-M and the University of Virginia ran supercomputer simulations to confirm that the combination was a good bet.
John Heron, co-corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at U-M, and Matthew Webb, a doctoral student in materials science and engineering, then carefully deposited the material using pulsed laser deposition to achieve precise layers with smooth interfaces. To make the material even more durable, they used oxides rather than conventional photonic materials; the oxides can be layered more precisely and are less likely to degrade under high heat.
"In previous work, traditional materials oxidized under high heat, losing their orderly layered structure," Heron said. "But when you start out with oxides, that degradation has essentially already taken place. That produces increased stability in the final layered structure."
After testing confirmed that the material worked as designed, Sean McSherry, first author of the study and a doctoral student in materials science and engineering at U-M, used computer modeling to identify hundreds of other combinations of materials that are also likely to work. While commercial implementation of the material tested in the study is likely years away, the core discovery opens up a new line of research into a variety of other nanophotonic materials that could help future researchers develop a range of new materials for a variety of applications.
The research was supported by the Department of Defense, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, grant number HR00112190005.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Katherine McAlpineUniversity of Michigan
Gabe CherryUniversity of Michigan
Copyright © University of Michigan
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Military
![]() NIST�s superconducting hardware could scale up brain-inspired computing October 7th, 2022
NIST�s superconducting hardware could scale up brain-inspired computing October 7th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Understanding outsize role of nanopores: New research reveals differences in pH, and more, about these previously mysterious environments August 26th, 2022
Understanding outsize role of nanopores: New research reveals differences in pH, and more, about these previously mysterious environments August 26th, 2022
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
Energy
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() The battery that runs 630 km on a single charge October 7th, 2022
The battery that runs 630 km on a single charge October 7th, 2022
![]() Conformal optical black hole for cavity September 30th, 2022
Conformal optical black hole for cavity September 30th, 2022
