

| Date | 23rd, Sep 2022 |
|---|
Home > Press > �Twisty� photons could turbocharge next-gen quantum communication: Team�s on-chip technology uses orbital angular momentum to encode more information into a single photon
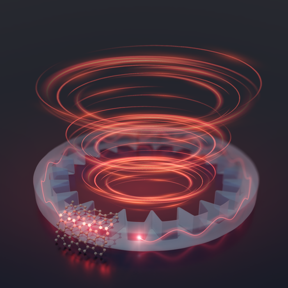 The image shows a quantum emitter capable of emitting single photons integrated with a geared-shaped resonator. By fine-tuning the arrangement of the emitter and the gear-shaped resonator, it�s possible to leverage the interaction between the photon�s spin and its orbital angular momentum to create individual �twisty� photons on demand.
CREDIT
Stevens Institute of Technology
The image shows a quantum emitter capable of emitting single photons integrated with a geared-shaped resonator. By fine-tuning the arrangement of the emitter and the gear-shaped resonator, it�s possible to leverage the interaction between the photon�s spin and its orbital angular momentum to create individual �twisty� photons on demand.
CREDIT
Stevens Institute of Technology
Abstract: Quantum computers and communication devices work by encoding information into individual or entangled photons, enabling data to be quantum securely transmitted and manipulated exponentially faster than is possible with conventional electronics. Now, quantum researchers at Stevens Institute of Technology have demonstrated a method for encoding vastly more information into a single photon, opening the door to even faster and more powerful quantum communication tools.
Hoboken, NJ | Posted on September 23rd, 2022
Typically, quantum communication systems �write� information onto a photon�s spin angular momentum. In this case, photons carry out either a right or left circular rotation, or form a quantum superposition of the two known as a two-dimensional qubit. It�s also possible to encode information onto a photon�s orbital angular momentum � the corkscrew path that light follows as it twists and torques forward, with each photon circling around the center of the beam. When the spin and angular momentum interlock, it forms a high-dimensional qudit -- enabling any of a theoretically infinite range of values to be encoded into and propagated by a single photon.
Qubits and qudits, also known as flying qubits and flying qudits, are used to propagate information stored in photons from one point to another. The main difference is that qudits can carry much more information over the same distance than qubits, providing the foundation for turbocharging next generation quantum communication.
In a cover story in the August 2022 issue of Optica, researchers led by Stefan Strauf, head of the NanoPhotonics Lab at Stevens, show that they can create and control individual flying qudits, or �twisty� photons, on demand � a breakthrough that could dramatically expand the capabilities of quantum communication tools. The work builds upon the team�s 2018 paper in Nature Nanotechnology.
�Normally the spin angular momentum and the orbital angular momentum are independent properties of a photon. Our device is the first to demonstrate simultaneous control of both properties via the controlled coupling between the two,� explained Yichen Ma, a graduate student in Strauf�s NanoPhotonics Lab, who led the research in collaboration with Liang Feng at the University of Pennsylvania, and Jim Hone at Columbia University.
�What makes it a big deal is that we�ve shown we can do this with single photons rather than classical light beams, which is the basic requirement for any kind of quantum communication application,� Ma said.
Encoding information into orbital angular momentum radically increases the information that can be transmitted, Ma explained. Leveraging �twisty� photons could boost the bandwidth of quantum communication tools, enabling them to transmit data far more quickly.
To create twisty photons, Strauf�s team used an atom-thick film of tungsten diselenide, an upcoming novel semiconductor material, to create a quantum emitter capable of emitting single photons.
Next, they coupled the quantum emitter in an internally reflective donut-shaped space called a ring resonator. By fine-tuning the arrangement of the emitter and the gear-shaped resonator, it�s possible to leverage the interaction between the photon�s spin and its orbital angular momentum to create individual �twisty� photons on demand. The key to enabling this spin-momentum-locking functionality relies in the gear-shaped patterning of the ring resonator, that when carefully engineered in the design, creates the twisty vortex beam of light that the device shoots out at the speed of light.
By integrating those capabilities into a single microchip measuring just 20 microns across � about a quarter of the width of a human hair � the team has created a twisty-photon emitter capable of interacting with other standardized components as part of a quantum communications system.
Some key challenges remain. While the team�s technology can control the direction in which a photon spirals � clockwise or anticlockwise � more work is needed to control the exact orbital angular momentum mode number. That�s the critical capability that will enable a theoretically infinite range of different values to be �written� into and later extracted from a single photon. Latest experiments in Strauf�s Nanophotonics Lab show promising results that this problem can be soon overcome, according to Ma.
Further work is also needed to create a device that can create twisted photons with rigorously consistent quantum properties, i.e., indistinguishable photons � a key requirement to enable the quantum internet. Such challenges affect everyone working in quantum photonics and could require new breakthroughs in material science to solve, Ma said.
�Plenty of challenges lie ahead,� he added. �But we�ve shown the potential for creating quantum light sources that are more versatile than anything that was previously possible.�
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:Thania BeniosStevens Institute of Technology
Office: 917-930-5988
Copyright © Stevens Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
News and information
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Quantum communication
![]() Quantum network nodes with warm atoms June 24th, 2022
Quantum network nodes with warm atoms June 24th, 2022
![]() Photonic integrated erbium doped amplifiers reach commercial performance: Boosting light power revolutionizes communications and autopilots June 17th, 2022
Photonic integrated erbium doped amplifiers reach commercial performance: Boosting light power revolutionizes communications and autopilots June 17th, 2022
![]() New hardware integrates mechanical devices into quantum tech April 22nd, 2022
New hardware integrates mechanical devices into quantum tech April 22nd, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Physicists from the University of Warsaw and the Military University of Technology have developed a new photonic system with electrically tuned topological features October 14th, 2022
Physicists from the University of Warsaw and the Military University of Technology have developed a new photonic system with electrically tuned topological features October 14th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Physicists from the University of Warsaw and the Military University of Technology have developed a new photonic system with electrically tuned topological features October 14th, 2022
Physicists from the University of Warsaw and the Military University of Technology have developed a new photonic system with electrically tuned topological features October 14th, 2022
![]() New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
New measurements quantifying qudits provide glimpse of quantum future October 14th, 2022
