

| Date | 14th, Oct 2022 |
|---|
Home > Press > Scientists count electric charges in a single catalyst nanoparticle down to the electron: Tenfold improvement in the sensitivity of electron holography reveals the net charge in a single platinum nanoparticle with a precision of just one electron, providing fundamental informatio
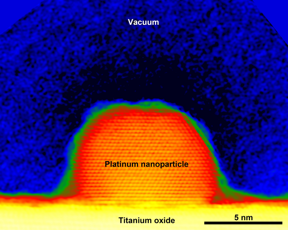 Ultrahigh sensitivity and precision electron holography measurements around a platinum nanoparticle like the one shown here have allowed scientists to count the net charge in a single catalyst nanoparticle with a precision of just one electron for the first time.
CREDIT
Murakami Lab, Kyushu University
Ultrahigh sensitivity and precision electron holography measurements around a platinum nanoparticle like the one shown here have allowed scientists to count the net charge in a single catalyst nanoparticle with a precision of just one electron for the first time.
CREDIT
Murakami Lab, Kyushu University
Abstract: If you often find yourself off by one when counting your socks after doing the laundry, you might want to sit down for this.
Fukuoka, Japan | Posted on October 14th, 2022
Scientists in Japan have now counted the number of extra�or missing�charges down to a precision of just one electron in single platinum nanoparticles having diameters only one-tenth those of common viruses.
This new process for precisely studying differences in net charge on metal nanoparticles will aid in the further understanding and development of catalysts for breaking down greenhouse and other harmful gases into fuels and benign gases or for efficiently producing ammonia needed for fertilizers used in agriculture.
Led by Kyushu University and Hitachi Ltd., the research team achieved this feat of extreme counting through hardware and software improvements that increased tenfold the sensitivity of a technique called electron holography.
While transmission electron microscopy uses a beam of electrons to observe materials down to the atomic level, electron holography utilizes the wave-like properties of electrons to probe electric and magnetic fields.
Interaction of an electron with fields causes a phase shift in its wave that can be identified by comparing it with a reference wave of an unaffected electron.
In the new work, the researchers focused their microscopes on single nanoparticles of platinum on a surface of titanium oxide, a combination of materials that is already known to act as a catalyst and speed up chemical reactions.
On average, the platinum nanoparticles had diameters of only 10 nm�so small that it would take nearly 100,000 to span one millimeter.
�While each particle contains a few tens of thousands of atoms of platinum, the addition or removal of just one or two negatively charged electrons causes significant changes in the behavior of the materials as catalysts,� says Ryotaro Aso, associate professor at Kyushu University�s Faculty of Engineering and first author on the paper in the journal Science reporting the work.
Measuring the fields just around a platinum nanoparticle�which vary depending on the imbalance of positive and negative charges in the particle�in an environment free of air, the researchers could determine the number of extra or missing electrons that are creating the fields.
�Amongst the millions of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons balancing each other out in the nanoparticle, we could successfully tell if the number of protons and electrons was different by just one,� explains Aso.
Although the fields are too weak to observe with previous methods, the researchers improved sensitivity by using a state-of-the-art 1.2-MV atomic-resolution holography microscope developed and operated by Hitachi that reduces mechanical and electrical noise and then processing the data to further tease out the signal from the noise.
Developed by Osaka University�s Yoshihiro Midoh, one of the paper�s co-authors, the signal processing technique utilized the so-called wavelet hidden Markov model (WHMM) to reduce the noise without also removing the extremely weak signals of interest.
In addition to identifying the charge state of individual nanoparticles, the researchers were able to relate differences in the number of electrons, which ranged from one to six, to differences in the crystal structure of the nanoparticles.
While the number of electrons per area has been previously reported by averaging over a large-area measurement of many particles, this is the first time scientists could measure a single electron difference in a single particle.
�By combining breakthroughs in microscopy hardware and signal processing, we are able to study phenomenon on increasingly smaller levels,� comments Yasukazu Murakami, professor at Kyushu University�s Faculty of Engineering and supervisor of the Kyushu U team.
�In this first demonstration, we measured the charge on a single nanoparticle in vacuum. In the future, we hope to overcome the challenges that currently prevent us from doing the same measurements in the presence of gas to get information in environments closer to actually applications.�
####
About Kyushu UniversityKyushu University is one of Japan�s leading research-oriented institutes of higher education since its founding in 1911. Home to around 19,000 students and 8,000 faculty and staff, Kyushu U's world-class research centers cover a wide range of study areas and research fields, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences. Its multiple campuses�including the largest in Japan�are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu that is frequently ranked among the world�s most livable cities and historically known as a gateway to Asia.
About Hitachi, Ltd.
Hitachi drives Social Innovation Business, creating a sustainable society with data and technology. We will solve customers� and society�s challenges with Lumada solutions leveraging IT, OT (Operational Technology) and products, under the business structure of Digital Systems & Services, Green Energy & Mobility, Connective Industries and Automotive Systems. Driven by green, digital, and innovation, we aim for growth through collaboration with our customers. The company�s consolidated revenues for fiscal year 2021 (ended March 31, 2022) totaled 10,264.6 billion yen ($84,136 million USD), with 853 consolidated subsidiaries and approximately 370,000 employees worldwide. For more information on Hitachi, please visit the company�s website at https://www.hitachi.com .
For more information, please click here
Contacts:William J. Potscavage Jr.Kyushu University
Office: +81-92-802-2138
Copyright © Kyushu University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
Chemistry
News and information
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() �Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
�Kagome� metallic crystal adds new spin to electronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
Improving the efficiency of nanogenerators that harvest static electricity October 28th, 2022
![]() New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
New era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics: Reviewing layered van-der-Waals ferroelectrics for future nanoelectronics October 28th, 2022
![]() Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Advanced Materials and NanoSystems: Theory and Experiment-Part 1 & 2 October 28th, 2022
Environment
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
![]() Ultrasmall VN/Co heterostructure with optimized N active sites anchored in N-doped graphitic nanocarbons for boosting hydrogen evolution September 30th, 2022
Ultrasmall VN/Co heterostructure with optimized N active sites anchored in N-doped graphitic nanocarbons for boosting hydrogen evolution September 30th, 2022
Automotive/Transportation
![]() The battery that runs 630 km on a single charge October 7th, 2022
The battery that runs 630 km on a single charge October 7th, 2022
![]() Silicon image sensor that computes: Device speeds up, simplifies image processing for autonomous vehicles and other applications August 26th, 2022
Silicon image sensor that computes: Device speeds up, simplifies image processing for autonomous vehicles and other applications August 26th, 2022
